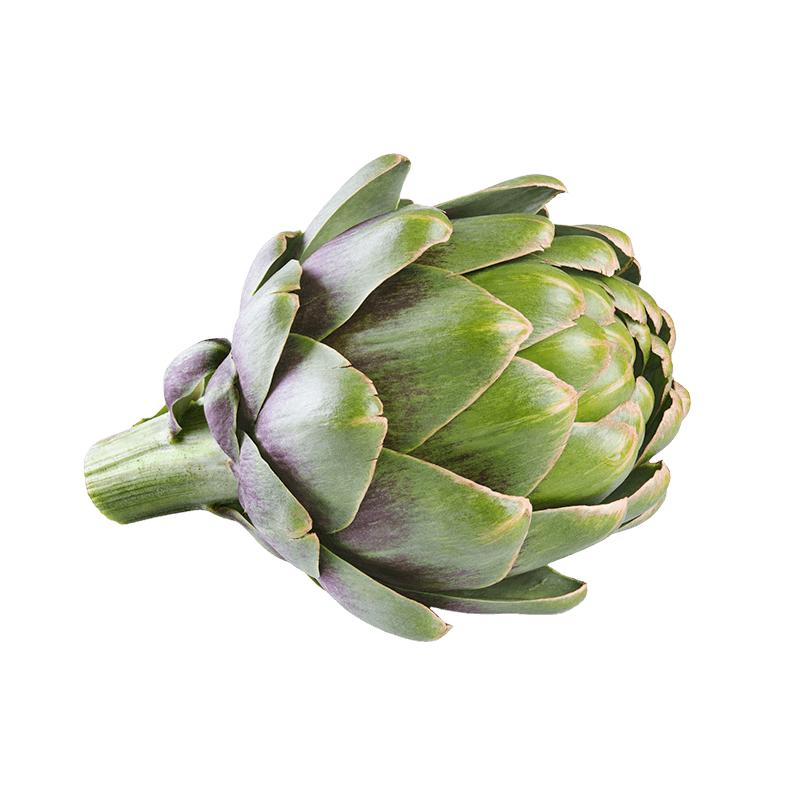

Alcachofa
Nombre latino
Origen
Parte utilzada
Ingredientes activos
Uso
La utilización de la alcachofa se remonta a la Antigüedad.
Es una de las verduras más antiguas de las que se cultivan en el mundo: por ejemplo, los griegos y romanos la cultivaban en su época de apogeo. Posteriormente, se utilizó también como planta ornamental en los jardines de los monasterios.
Su receptáculo carnoso y la base de las brácteas son comestibles como verdura, mientras que las hojas se reservan para la fitoterapia y la preparación de aperitivos. La alcachofa es rica en antioxidantes y, por lo tanto, protege contra los radicales libres.1 La alcachofa facilita la desintoxicación y la función hepática. 2,4Protege el hígado de los efectos de las sustancias tóxicas. 5,11
Además, la planta es conocida por estimular la digestión y por mantener el bienestar intestinal.12-15
Referencias bibliográficas
- Antioxidative and protective properties of extracts from leaves of the artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) against hydroperoxide-induced oxidative stress in cultured rat hepatocytes.
Gebhardt R.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1997 Jun;144(2):279-86.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9194411
- Increase in choleresis by means of artichoke extract.
Kirchhoff R, Beckers C, Kirchhoff GM, Trinczek-Gärtner H, Petrowicz O, Reimann HJ. Phytomedicine. 1994 Sep;1(2):107-15.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23195882
- Artichoke leaf extract - Recent findings reflecting effects on lipid metabolism, liver and gastrointestinal tracts.
Kraft K.
Phytomedicine. 1997 Dec;4(4):369-78.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23195590
- Anticholestatic activity of flavonoids from artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) and of their metabolites.
Gebhardt R.
Med Sci Monit. 2001 May;7 Suppl 1:316-20.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12211745
- Hepatoprotective activity of polyphenolic compounds from Cynara scolymus against CCl4 toxicity in isolated rat hepatocytes
Adzet T, Camarasa J, Laguna JC.
J Nat Prod. 1987 Jul-Aug;50(4):612-7.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3430163
- Effect of pretreatment with artichoke extract on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury and oxidative stress.
Mehmetçik G, Ozdemirler G, Koçak-Toker N, Cevikbaş U, Uysal M.
Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2008 Sep;60(6):475-80.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18583118
- Choleretic activity and biliary elimination of lipids and bile acids induced by an artichoke leaf extract in rats.
Saénz Rodriguez T, García Giménez D, de la Puerta Vázquez R.
Phytomedicine. 2002 Dec;9(8):687-93.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12587687
- Efficacy of different Cynara scolymus preparations on liver complaints.
Speroni E, Cervellati R, Govoni P, Guizzardi S, Renzulli C, Guerra MC.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2003 Jun;86(2-3):203-11.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12738088
- Protective properties of artichoke (Cynara scolymus) against oxidative stress induced in cultured endothelial cells and monocytes.
Zapolska-Downar D, Zapolski-Downar A, Naruszewicz M, Siennicka A, Krasnodebska B, Kołdziej B.
Life Sci. 2002 Nov 1;71(24):2897-08.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12377270
10. Chem Biol Interact. 2008 May 28;173(2):77-83.
Efficacy of caffeic acid in preventing nickel induced oxidative damage in liver of rats.
Pari L, Prasath A.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18405891
- Liver fibrosis in mice induced by carbon tetrachloride and its reversion by luteolin.
Domitrović R, Jakovac H, Tomac J, Sain I.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009 Dec 15;241(3):311-21.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19747501
- Efficacy of artichoke leaf extract in the treatment of patients with functional dyspepsia: a six-week placebo-controlled, double-blind, multicentre trial.
Holtmann G, Adam B, Haag S, Collet W, Grünewald E, Windeck T.
Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003 Dec;18(11-12):1099-105.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14653829
- Artichoke leaf extract reduces symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome and improves quality of life in otherwise healthy volunteers suffering from concomitant dyspepsia: a subset analysis.
Bundy R, Walker AF, Middleton RW, Marakis G, Booth JC.
J Altern Complement Med. 2004 Aug;10(4):667-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15353023
- A double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over study to establish the bifidogenic effect of a very-long-chain inulin extracted from globe artichoke (Cynara scolymus) in healthy human subjects.
Costabile A, Kolida S, Klinder A, Gietl E, Bäuerlein M, Frohberg C, Landschütze V, Gibson GR.
Br J Nutr. 2010 Oct;104(7):1007-17.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20591206
- Artichoke leaf extract reduces mild dyspepsia in an open study.
Marakis G, Walker AF, Middleton RW, Booth JC, Wright J, Pike DJ.
Phytomedicine. 2002 Dec;9(8):694-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12587688
Las declaraciones de propiedades saludables relativas a las plantas que contienen los productos que figuran en nuestro sitio web son conformes a la lista de declaraciones de propiedades saludables en espera de evaluación definitiva por parte de las autoridades comunitarias (véase el sitio web de la Comisión Europea: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/). Sin embargo, pueden sufrir modificaciones tras su evaluación por las autoridades nacionales competentes.
Las declaraciones de propiedades saludables relativas a otros nutrientes o sustancias que contienen los productos que figuran en nuestro sitio web son conformes al Reglamento n.º 432/2012 de la Comisión, de 16 de mayo de 2012, por el que se establece una lista de declaraciones autorizadas de propiedades saludables de los alimentos distintas de las relativas a la reducción del riesgo de enfermedad y al desarrollo y la salud de los niños (véase el sitio web de la Comisión Europea: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/).

 Belgique
Belgique  België
België  France
France  Italia
Italia  Portugal
Portugal  España
España  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Κύπρος
Κύπρος 




