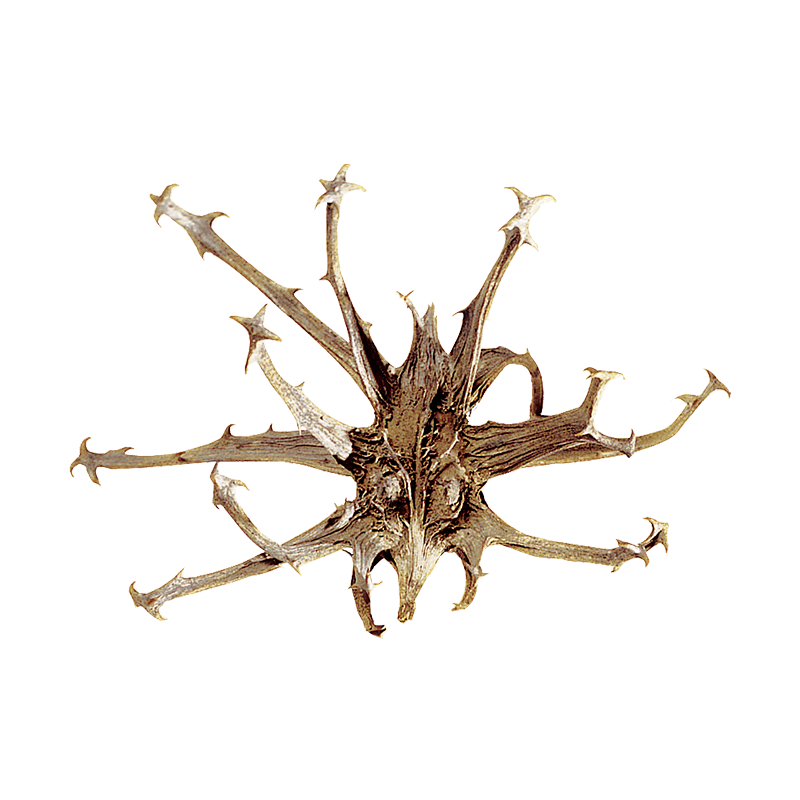

Harpagófito o garra del diablo
Nombre latino
Origen
Parte utilzada
Ingredientes activos
Ácidos fenólicos: antioxidante.
Flavonoides: antioxidantes.
Uso
La garra del diablo se convirtió en el objeto de muchos estudios científicos en la década de 1950, cuando científicos alemanes empezaron a interesarse por los medicamentos namibios tradicionales.
Desde entonces, se han utilizado preparados con tubérculos para tratar las artrosis dolorosas, las tendinitis, la gota, el lumbago, la mialgia, la dispepsia, la pérdida de apetito y como terapia de mantenimiento de los reumatismos degenerativos. Hasta la década de 1990 se sabía poco sobre las sustancias activas concretas, sus efectos exactos y su eficacia. A partir de ese momento, otros estudios posteriores demostraron que algunos extractos de harpagófito son eficaces y se pueden usar con seguridad.
La utilización de la garra del diablo está respaldada científicamente en la actualidad gracias a su acción suavizante1-21 en el caso de las molestias en las articulaciones22-33 y dolores en la parte baja de la espalda34-40. El extracto de esta planta también puede aplicarse en cremas o geles de uso externo. 41-43
Referencias bibliográficas
- Community herbal monograph on Harpagophytum procumbens DC. and/or Harpagophytum zeyheri Decne, Radix
Committee On Herbal Medicinal Products (HMPC)
Doc. Ref.: EMEA/HMPC/251323/2006
http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Herbal_-_Community_herbal_monograph/2010/01/WC500059018.pdf - Formation of nitrogen-containing metabolites from the main iridoids of Harpagophytum procumbens and H. zeyheri by human intestinal bacteria
Baghdikian B., Guiraud-Dauriac H., Ollivier E., N’Guyen A., Dumenil G., Balansard G.
Planta medica 1999 ; 65 (2): 164–166.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10193209 - Harpagophytum procumbens (Devil's Claw): A Possible Natural Anti-Inflammatory Agent (An Experimental Study)
Mohamad Ibrahim Ahmed, Mohamad Ismael Afifi, Ibrahim Hamdy Younos
Bioline: http://www.bioline.org.br/pdf?pt05013 - Inhibition of TNF-alpha synthesis in LPS-stimulated primary human monocytes by Harpagophytum extract SteiHap 69.
Fiebich BL, Heinrich M, Hiller KO, Kammerer N.
Phytomedicine. 2001 Jan;8(1):28-30.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11292236 - Harpagoside suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced iNOS and COX-2 expression through inhibition of NF-kappa B activation.
Huang TH, Tran VH, Duke RK, Tan S, Chrubasik S, Roufogalis BD, Duke CC.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2006 Mar 8;104(1-2):149-55.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16203115 - Downregulation of iNOS expression in rat mesangial cells by special extracts of Harpagophytum procumbens derives from harpagoside-dependent and independent effects.
Kaszkin M, Beck KF, Koch E, Erdelmeier C, Kusch S, Pfeilschifter J, Loew D.
Phytomedicine. 2004 Nov;11(7-8):585-95.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15636171 - Harpagophytum procumbens suppresses lipopolysaccharide-stimulated expressions of cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase in fibroblast cell line L929.
Jang MH, Lim S, Han SM, Park HJ, Shin I, Kim JW, Kim NJ, Lee JS, Kim KA, Kim CJ.
J Pharmacol Sci. 2003 Nov;93(3):367-71.
J-STAGE: https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jphs/93/3/93_3_367/_pdf - Devil's Claw-a review of the ethnobotany, phytochemistry and biological activity of Harpagophytum procumbens.
Mncwangi N, Chen W, Vermaak I, Viljoen AM, Gericke N.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Oct 11;143(3):755-71.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22940241 - Molecular targets of the antiinflammatory Harpagophytum procumbens (devil's claw): inhibition of TNFα and COX-2 gene expression by preventing activation of AP-1.
Fiebich BL, Muñoz E, Rose T, Weiss G, McGregor GP.
Phytother Res. 2012 Jun;26(6):806-11.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22072539 - Effect of isolated fractions of Harpagophytum procumbens D.C. (devil's claw) on COX-1, COX-2 activity and nitric oxide production on whole-blood assay.
Anauate MC, Torres LM, de Mello SB.
Phytother Res. 2010 Sep;24(9):1365-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20812280 - Isolation and anti-inflammatory activity evaluation of triterpenoids and a monoterpenoid glycoside from Harpagophytum procumbens.
Qi J, Li N, Zhou JH, Yu BY, Qiu SX.
Planta Med. 2010 Nov;76(16):1892-6.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20577946 - Inhibitory effects of devil's claw (secondary root of Harpagophytum procumbens) extract and harpagoside on cytokine production in mouse macrophages.
Inaba K, Murata K, Naruto S, Matsuda H.
J Nat Med. 2010 Apr;64(2):219-22.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20177800 - The inhibition of free radical generation by preparations of Harpagophytum procumbens in vitro.
Grant L, McBean DE, Fyfe L, Warnock AM.
Phytother Res. 2009 Jan;23(1):104-10.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18803229 - Antinociceptive effects of St. John's wort, Harpagophytum procumbens extract and Grape seed proanthocyanidins extract in mice.
Uchida S, Hirai K, Hatanaka J, Hanato J, Umegaki K, Yamada S.
Biol Pharm Bull. 2008 Feb;31(2):240-5.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18239280 J-STAGE: https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/bpb/31/2/31_2_240/_pdf - Iridoid glycosides from Harpagophytum procumbens D.C. (devil's claw).
Qi J, Chen JJ, Cheng ZH, Zhou JH, Yu BY, Qiu SX.
Phytochemistry. 2006 Jul;67(13):1372-7.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16857222 - Analgesic, antiinflammatory and antidiabetic properties of Harpagophytum procumbens DC (Pedaliaceae) secondary root aqueous extract.
Mahomed IM, Ojewole JA.
Phytother Res. 2004 Dec;18(12):982-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15742343 - Effects of Harpagophytum procumbens LI 174 (devil's claw) on sensory, motor und vascular muscle reagibility in the treatment of unspecific back pain.
Göbel H, Heinze A, Ingwersen M, Niederberger U, Gerber D.
Schmerz. 2001 Feb;15(1):10-8.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11810324 - New and known iridoid- and phenylethanoid glycosides from Harpagophytum procumbens and their in vitro inhibition of human leukocyte elastase.
Boje K, Lechtenberg M, Nahrstedt A.
Planta Med. 2003 Sep;69(9):820-5.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14598207 - Effect of a Harpagophytum procumbens DC extract on matrix metalloproteinases in human chondrocytes in vitro.
Schulze-Tanzil G, Hansen C, Shakibaei M.
Arzneimittelforschung. 2004;54(4):213-20.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15146934?dopt=Abstract - Investigations on the pharmacokinetic properties of Harpagophytum extracts and their effects on eicosanoid biosynthesis in vitro and ex vivo.
Loew D, Möllerfeld J, Schrödter A, Puttkammer S, Kaszkin M.
Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2001 May;69(5):356-64.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11372004 - Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of an aqueous extract of Harpagophytum procumbens.
Lanhers MC, Fleurentin J, Mortier F, Vinche A, Younos C.
Planta Med. 1992 Apr;58(2):117-23.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1529021 - Harpagophytum und Harpagophytum-Präparate in der Schweiz
Dr. Christoph Bachmann
Phytotherapie Nr. 3 • 2004
ASTRAL: http://phyto.astral.ch/Phyto/ALL/phytotherapie/003-2004/05-harpagophym-praep-CH.pdf - A review of the biological and potential therapeutic actions of Harpagophytum procumbens.
Grant L, McBean DE, Fyfe L, Warnock AM.
Phytother Res. 2007 Mar;21(3):199-209.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17128436 - An analytical study, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of Harpagophytum procumbens and Harpagophytum zeyheri.
Baghdikian B, Lanhers MC, Fleurentin J, Ollivier E, Maillard C, Balansard G, Mortier F.
Planta Med. 1997 Apr;63(2):171-6.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9140234 - Degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system--overview of current clinical studies of Devil's Claw (Harpagophyti radix).
Wegener T.
Wien Med Wochenschr. 2002;152(15-16):389-92.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12244884 - Harpagoside: from Kalahari Desert to pharmacy shelf.
Georgiev MI, Ivanovska N, Alipieva K, Dimitrova P, Verpoorte R.
Phytochemistry. 2013 Aug;92:8-15.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23642455 - Estimation of the relative antiinflammatory efficacies of six commercial preparations of Harpagophytum procumbens (Devil's Claw).
Ouitas NA, Heard C.
Phytother Res. 2010 Mar;24(3):333-8.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19610038 - Herbal medicine for low back pain: a Cochrane review.
Gagnier JJ, van Tulder MW, Berman B, Bombardier C.
Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007 Jan 1;32(1):82-92.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17202897 - Efficacy and tolerance of Harpagophytum procumbens versus diacerhein in treatment of osteoarthritis.
Chantre P, Cappelaere A, Leblan D, Guedon D, Vandermander J, Fournie B.
Phytomedicine. 2000 Jun;7(3):177-83.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11185727 - Treatment of patients with arthrosis of hip or knee with an aqueous extract of devil's claw (Harpagophytum procumbens DC.).
Wegener T, Lüpke NP.
Phytother Res. 2003 Dec;17(10):1165-72.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14669250 - Zur klinischen Wirksamkeit der südafrikanischen Teufelskrallenwurzel (Harpagophyti radix) bei Patienten mit Cox- und Gonarthrose: Ergebnisse und Bewertung einer klinischen Studie der Phase IV.
Tankred Wegener
Universität Osnabrück Repositorium urn:nbn:de:gbv:700-2006052225
Universität Osnabrück: http://d-nb.info/980109957/34 - Effectiveness and safety of Devil's Claw tablets in patients with general rheumatic disorders.
Warnock M, McBean D, Suter A, Tan J, Whittaker P.
Phytother Res. 2007 Dec;21(12):1228-33.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17886223 - Effectiveness of devil's claw for osteoarthritis.
Chrubasik S, Pollak S, Black A.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 2002 Nov;41(11):1332-3; author reply 1333.
Oxford Journals: http://rheumatology.oxfordjournals.org/content/41/11/1332.full.pdf+html - Effectiveness of Harpagophytum procumbens in treatment of acute low back pain.
Chrubasik S, Zimpfer C, Schütt U, Ziegler R.
Phytomedicine. 1996 May;3(1):1-10.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23194854 - Wirksamkeit und Wirtschaftlichkeit von Teufelskrallenwurzelextrakt bei Rückenschmerzen: Erste Ergebnisse einer therapeutischen Kohortenstudie.
Chrubasik S., Schmidt A., Junck H., Pfisterer
Forsch. Komplementärmed. 1997; 4: 332–336.
KARGER: http://www.karger.com/Article/Abstract/210360 - Effectiveness of Harpagophytum extract WS 1531 in the treatment of exacerbation of low back pain: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study.
Chrubasik S, Junck H, Breitschwerdt H, Conradt C, Zappe H.
Eur J Anaesthesiol. 1999 Feb;16(2):118-29.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10101629 - A randomized double-blind pilot study comparing Doloteffin and Vioxx in the treatment of low back pain.
S Chrubasik, A Model, A Black, S Pollak
Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003 Jan ;42 (1):141-8 12509627 Cit:24
BioInfoBank Library: http://lib.bioinfo.pl/paper:12509627 - A 1-year follow-up after a pilot study with Doloteffin for low back pain.
Chrubasik S, Künzel O, Thanner J, Conradt C, Black A.
Phytomedicine. 2005 Jan;12(1-2):1-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15693701 - Comparison of outcome measures during treatment with the proprietary Harpagophytum extract doloteffin in patients with pain in the lower back, knee or hip.
Chrubasik S, Thanner J, Künzel O, Conradt C, Black A, Pollak S.
Phytomedicine. 2002 Apr;9(3):181-94.
Joint s.a.s.: http://www.joint-biomateriali.it/admin/upload/documents/Doc13_Comparison%20of%20outcome%20measures%20during%20treatment.pdf - Harpgophytum procumbens for osteoarthritis and low back pain: a systematic review.
Gagnier JJ, Chrubasik S, Manheimer E.
BMC Complement Altern Med. 2004 Sep 15;4:13.
PMC: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC520753/pdf/1472-6882-4-13.pdf - A novel ex vivo skin model for the assessment of the potential transcutaneous anti-inflammatory effect of topically applied Harpagophytum procumbens extract.
Ouitas NA, Heard CM.
Int J Pharm. 2009 Jul 6;376(1-2):63-8.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19383533 - Dermal and transcutaneous delivery of the major glycoside constituents of Harpagophytum procumbens (Devil's Claw) in vitro.
Abdelouahab N, Heard CM.
Planta Med. 2008 Apr;74(5):527-31.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18401847 - Effect of the major glycosides of Harpagophytum procumbens (Devil's Claw) on epidermal cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in vitro.
Abdelouahab N, Heard C.
J Nat Prod. 2008 May;71(5):746-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18412394
Las declaraciones de propiedades saludables relativas a las plantas que contienen los productos que figuran en nuestro sitio web son conformes a la lista de declaraciones de propiedades saludables en espera de evaluación definitiva por parte de las autoridades comunitarias (véase el sitio web de la Comisión Europea: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/). Sin embargo, pueden sufrir modificaciones tras su evaluación por las autoridades nacionales competentes.
Las declaraciones de propiedades saludables relativas a otros nutrientes o sustancias que contienen los productos que figuran en nuestro sitio web son conformes al Reglamento n.º 432/2012 de la Comisión, de 16 de mayo de 2012, por el que se establece una lista de declaraciones autorizadas de propiedades saludables de los alimentos distintas de las relativas a la reducción del riesgo de enfermedad y al desarrollo y la salud de los niños (véase el sitio web de la Comisión Europea: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/).

 Belgique
Belgique  België
België  France
France  Italia
Italia  Portugal
Portugal  España
España  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Κύπρος
Κύπρος