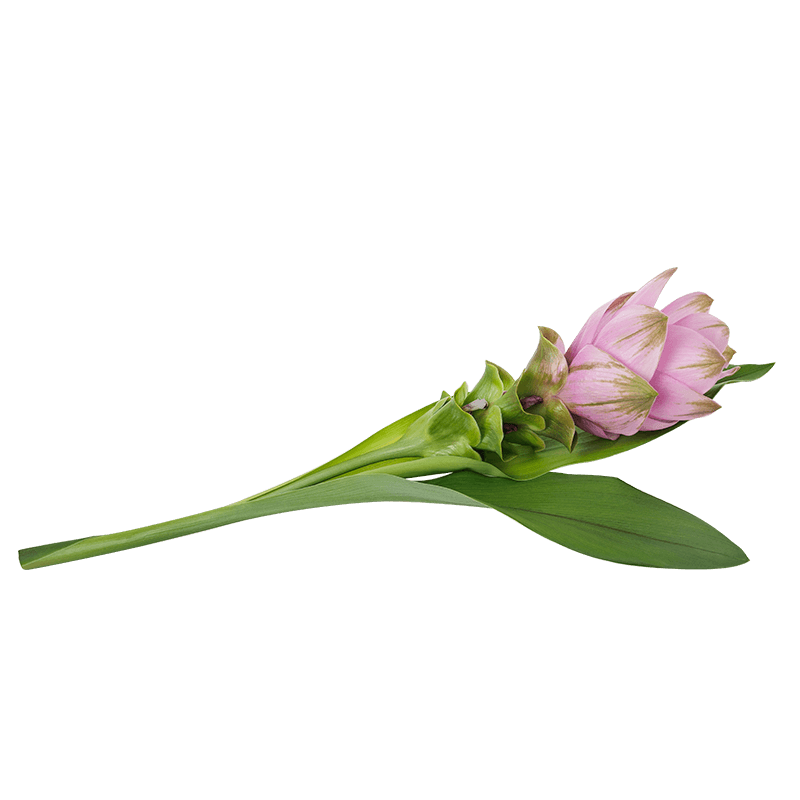
Curcuma
Pianta perenne e robusta che può raggiungere i 90 cm di altezza. Le foglie sono grandi, verdi, oblunghe e affusolate. I fiori, di colore giallo pallido, sono riuniti in spighe. Il rizoma fresco ha la buccia beige e la polpa di colore arancione acceso.
Nome latino
Origine
Asia meridionale - India
Parte utilizzata
I rizomi.
Principi attivi
Curcumine: polifenoli ad azione antiossidante e antinfiammatoria
Caroteni: antiossidanti idrosolubili.
Olio essenziale: responsabile dell’aroma.
Uso
La curcuma è uno dei principali ingredienti di molti piatti asiatici ed anche del curry in polvere. Ha un sapore terroso, leggermente pepato e un odore simile alla senape.
La curcuma è un conservante e un colorante naturale.
Nell’Europa medioevale, la curcuma era nota con il nome di "zafferano delle Indie", siccome veniva ampiamente utilizzata come alternativa allo zafferano, spezia molto più costosa, per colorare i cibi. Oggi la curcuma è utilizzata per colorare formaggi, yogurt, burro e margarina. La curcuma è inoltre impiegata per accentuare il colore giallo di alcune senapi e altri prodotti alimentari.
La curcuma è attualmente utilizzata per tingere i tessuti per indumenti come i sari e le tuniche dei monaci buddisti. Presso alcune popolazioni, viene cosparsa sul corpo in occasione di particolari riti.
Da secoli la curcuma è utilizzata nella medicina ayurvedica e cinese.
In India, veniva tradizionalmente utilizzata per curare problemi di stomaco e disturbi epatici, nonché per guarire le ferite e regolarizzare il flusso mestruale.
Le curcumine, dei composti polifenolici, sono le principali responsabili della maggior parte degli effetti sulla salute. Studi clinici hanno dimostrato che l’utilizzo della curcumina non presenta controindicazioni, neppure a dosaggio elevato pari a 12 g/giorno nell’uomo, ma presenta una lieve biodisponibilità. Questo è da imputare ad un modesto assorbimento orale dovuto alla sua solubilità nell’acqua estremamente bassa e a un metabolismo presistemico di questa molecola.
Per migliorare la biodisponibilità della curcumina, sono state adottate diverse possibili soluzioni. Questi approcci si basano, prima di tutto, sull’utilizzo di additivi come la piperina. Oggi si ottengono risultati decisamente migliori mediante microinclusione della molecola nella beta-ciclodestrina o nei fitosomi.
Grazie alle sua azione antiossidante, la curcumina offre una protezione cellulare all’organismo. 1-10 Aiuta a gestire le risposte antinfiammatorie. 11-63
Aiuta a mantenere una buona salute e un corretto funzionamento del fegato 64-98 e del sistema digestivo. 99-132
La curcumina contribuisce al corretto funzionamento del sistema locomotore. Aiuta a proteggere e a mantenere la flessibilità di articolazioni, tendini e muscoli e ad alleviare i dolori di natura infiammatoria. 133-153
Referenze bibliografiche
- Antioxidant food supplements and obesity-related inflammation.
Mangge H, Summers K, Almer G, Prassl R, Weghuber D, Schnedl W, Fuchs D.
Curr Med Chem. 2013;20(18):2330-7.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23531214 - Free radical scavenging activity of curcuminoids.
Sreejayan N, Rao MN.
Arzneimittelforschung. 1996 Feb;46(2):169-71.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8720307 - Discovery of Curcumin, a Component of the Golden Spice, and Its Miraculous Biological Activities
Gupta SC, Patchva S, Koh W, Aggarwal BB.
Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2012 Mar;39(3):283-99.
PMC: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3288651/ - Antioxidant Curcuma extracts decrease the blood lipid peroxide levels of human subjects
Ana Ramirez-Boscá, Alfonso Soler, Miguel Angel Carrión Gutierrez, Juan Laborda Alvarez, Eliseo Quintanilla Almagro
Journal of the American Aging Association 09/1995; 18(4):167-169.
ResearchGate: http://www.researchgate.net/publication/225480131_Antioxidant_Curcuma_extracts_decrease_the_blood_lipid_peroxide_levels_of_human_subjects - Protective effect of dietary curcumin and capsaicin on induced oxidation of low-density lipoprotein, iron-induced hepatotoxicity and carrageenan-induced inflammation in experimental rats.
Manjunatha H, Srinivasan K.
FEBS J. 2006 Oct;273(19):4528-37.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16956363 - Nitric oxide scavenging by curcuminoids.
Sreejayan, Rao MN.
J Pharm Pharmacol. 1997 Jan;49(1):105-7.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9120760 - Protective effect of curcumin on experimentally induced inflammation, hepatotoxicity and cardiotoxicity in rats: evidence of its antioxidant property.
Naik SR, Thakare VN, Patil SR.
Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2011 Jul;63(5):419-31.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20363603 - The promise of slow down ageing may come from curcumin.
Sikora E, Bielak-Zmijewska A, Mosieniak G, Piwocka K.
Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16(7):884-92.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20388102 - Curcumin, inflammation, ageing and age-related diseases.
Sikora E, Scapagnini G, Barbagallo M.
Immun Ageing. 2010 Jan 17;7(1):1.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20205886 - Phase I clinical trials of curcumin, a chemopreventative agent in patients with high-risk or pre-malignant lesions.
Cheng AL, Hsu CH, Lin JK, et al.
Anticancer Res. 2001;21:2895-2900.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11712783 - Curcumin in inflammatory diseases.
Shehzad A, Rehman G, Lee YS.
Biofactors. 2013 Jan-Feb;39(1):69-77.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23281076 - Inhibition of 5-hydroxy-eicosatetraenoic acid (5-HETE) formation in intact human neutrophils by naturally-occurring diarylheptanoids: inhibitory activities of curcuminoids and yakuchinones.
Flynn DL, Rafferty MF, Boctor AM.
Prostaglandins Leukot Med. 1986 Jun;22(3):357-60.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3460103 - Curcumin, a major component of food spice turmeric (Curcuma longa) inhibits aggregation and alters eicosanoid metabolism in human blood platelets.
Srivastava KC, Bordia A, Verma SK.
Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1995 Apr;52(4):223-7.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7784468 - Mechanism of antiinflammatory actions of curcumine and boswellic acids.
Ammon HP, Safayhi H, Mack T, Sabieraj J.
J Ethnopharmacol. 1993 Mar;38(2-3):113-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8510458 - Inhibition of neutrophil response by curcumin.
Srivastava R.
Agents Actions. 1989 Nov;28(3-4):298-303.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2556903 - Curcumin inhibition of inflammatory cytokine production by human peripheral blood monocytes and alveolar macrophages.
Abe Y, Hashimoto S, Horie T.
Pharmacol Res. 1999 Jan;39(1):41-7.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10051376 - Effect of curcumin and capsaicin on arachidonic acid metabolism and lysosomal enzyme secretion by rat peritoneal macrophages.
Joe B, Lokesh BR.
Lipids. 1997 Nov;32(11):1173-80.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9397403 - Curcumin, a Curcuma longa constituent, acts on MAPK p38 pathway modulating COX-2 and iNOS expression in chronic experimental colitis.
Camacho-Barquero L, Villegas I, Sánchez-Calvo JM, Talero E, Sánchez-Fidalgo S, Motilva V, Alarcón de la Lastra C.
Int Immunopharmacol. 2007 Mar;7(3):333-42.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17276891 - Enhancement of wound healing by curcumin in animals.
Sidhu GS, Singh AK, Thaloor D, Banaudha KK, Patnaik GK, Srimal RC, Maheshwari RK.
Wound Repair Regen. 1998 Mar-Apr;6(2):167-77.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9776860 - Effects of dietary fats and curcumin on IgE-mediated degranulation of intestinal mast cells in brown Norway rats.
Ju HR, Wu HY, Nishizono S, Sakono M, Ikeda I, Sugano M, Imaizumi K.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1996 Nov;60(11):1856-60.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8987863 - Efficacy of curcumin in the management of chronic anterior uveitis.
Lal B, Kapoor AK, Asthana OP, Agrawal PK, Prasad R, Kumar P, Srimal RC.
Phytother Res. 1999 Jun;13(4):318-22.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10404539 - Role of curcumin in idiopathic inflammatory orbital pseudotumours.
Lal B, Kapoor AK, Agrawal PK, Asthana OP, Srimal RC.
Phytother Res. 2000;14:443-447.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10960899 - Regulation of inflammation and redox signaling by dietary polyphenols.
Rahman I, Biswas SK, Kirkham PA.
Biochem Pharmacol. 2006 Nov 30;72(11):1439-52.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16920072 - Curcumin as "Curecumin": from kitchen to clinic.
Goel A, Kunnumakkara AB, Aggarwal BB.
Biochem Pharmacol. 2008 Feb 15;75(4):787-809.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17900536 - Multi-targeted therapy by curcumin: how spicy is it?
Goel A, Jhurani S, Aggarwal BB.
Mol Nutr Food Res. 2008 Sep;52(9):1010-30.
Curcumin in New Zealand: http://www.curcumin.co.nz/pdf/Curcumin_Multi-Targeted_Thereapy.pdf - Curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, bisdemethoxycurcumin, tetrahydrocurcumin and turmerones differentially regulate anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative responses through a ROS-independent mechanism
Santosh K. Sandur, Manoj K. Pandey, Bokyung Sung, Kwang Seok Ahn, Akira Murakami1, Gautam Sethi, Pornngarm Limtrakul2, Vladimir Badmaev3 and Bharat B. Aggarwal
Carcinogenesis (2007) 28 (8): 1765-1773.
Oxford Journals: http://carcin.oxfordjournals.org/content/28/8/1765.full - Evaluation of anti-inflammatory property of curcumin (diferuloyl methane) in patients with postoperative inflammation.
Satoskar RR, Shah SJ, Shenoy SG.
Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1986 Dec;24(12):651-4.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3546166 - Activation of transcription factor NF-kappa B is suppressed by curcumin (diferuloylmethane).
Singh S, Aggarwal BB.
J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 20;270(42):24995-5000.
The Journal of Biological Chemistry: http://www.jbc.org/content/270/42/24995.full.pdf+html - Inhibitory effects of curcumin on in vitro lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase activities in mouse epidermis.
Huang MT, Lysz T, Ferraro T, Abidi TF, Laskin JD, Conney AH.
Cancer Res. 1991 Feb 1;51(3):813-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1899046 - Curcumin, an anti-tumour promoter and anti-inflammatory agent, inhibits induction of nitric oxide synthase in activated macrophages.
Brouet I, Ohshima H.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Jan 17;206(2):533-40.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7530002 - Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor by curcumin, a phytochemical.
Chan MM.
Biochem Pharmacol. 1995 May 26;49(11):1551-6.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7786295 - Molecular mechanisms underlying chemopreventive activities of anti-inflammatory phytochemicals: down-regulation of COX-2 and iNOS through suppression of NF-kappa B activation.
Surh YJ, Chun KS, Cha HH, Han SS, Keum YS, Park KK, Lee SS.
Mutat Res. 2001 Sep 1;480-481:243-68.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11506818 - Targeting inflammation-induced obesity and metabolic diseases by curcumin and other nutraceuticals.
Aggarwal BB.
Annu Rev Nutr. 2010 Aug 21;30:173-99.
PMC: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3144156/ - Cyclodextrin-complexed curcumin exhibits anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative activities superior to those of curcumin through higher cellular uptake.
Yadav VR, Prasad S, Kannappan R, Ravindran J, Chaturvedi MM, Vaahtera L, Parkkinen J, Aggarwal BB.
Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Oct 1;80(7):1021-32.
PMC: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2923254/ - Potential therapeutic effects of curcumin, the anti-inflammatory agent, against neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, pulmonary, metabolic, autoimmune and neoplastic diseases.
Aggarwal BB, Harikumar KB.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Jan;41(1):40-59.
Curcumin Research: http://www.curcuminresearch.org/PDF/Aggarwal%20BB-2.pdf - Curcumin attenuates allergic airway inflammation by regulation of CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells (Tregs)/Th17 balance in ovalbumin-sensitized mice.
Ma C, Ma Z, Fu Q, Ma S.
Fitoterapia. 2013 Jun;87:57-64.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23500387 - Modulation of adipose tissue inflammation by bioactive food compounds.
Siriwardhana N, Kalupahana NS, Cekanova M, LeMieux M, Greer B, Moustaid-Moussa N.
J Nutr Biochem. 2013 Apr;24(4):613-23.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23498665 - Curcumin modulates the inflammatory response and inhibits subsequent fibrosis in a mouse model of viral-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Avasarala S, Zhang F, Liu G, Wang R, London SD, London L.
PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57285.
PMC: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3577717/ - Curcumin: An Orally Bioavailable Blocker of TNF and Other Pro-inflammatory Biomarkers.
Aggarwal BB, Gupta SC, Sung B.
Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Feb 20.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23425071 - Curcumin alleviates oxidative stress, inflammation, and renal fibrosis in remnant kidney through the Nrf2-keap1 pathway.
Soetikno V, Sari FR, Lakshmanan AP, Arumugam S, Harima M, Suzuki K, Kawachi H, Watanabe K.
Mol Nutr Food Res. 2012 Nov 23.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23174956 - A randomized controlled trial on the anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin in patients with chronic sulphur mustard-induced cutaneous complications.
Panahi Y, Sahebkar A, Parvin S, Saadat A.
Ann Clin Biochem. 2012 Nov;49(Pt 6):580-8.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23038702 - Anti-inflammatory potential of curcumin and quercetin in rats: Role of oxidative stress, heme oxygenase-1 and TNF-α
Heeba GH, Mahmoud ME, El Hanafy AA.
Toxicol Ind Health. 2012 Sep 28.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23024111 - Curcumin suppresses ovalbumin-induced allergic conjunctivitis.
Chung SH, Choi SH, Choi JA, Chuck RS, Joo CK.
Mol Vis. 2012;18:1966-72.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22876123 - Curcumin inhibits inflammatory response and bone loss during experimental periodontitis in rats.
Zhou T, Chen D, Li Q, Sun X, Song Y, Wang C.
Acta Odontol Scand. 2013 Mar;71(2):349-56.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22554269 - Neuroprotective effect of curcuminoids against inflammation-mediated dopaminergic neurodegeneration in the MPTP model of Parkinson's disease.
Ojha RP, Rastogi M, Devi BP, Agrawal A, Dubey GP.
J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2012 Sep;7(3):609-18.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22527634 - Curcumin attenuates TNF-α-induced expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and proinflammatory cytokines in human endometriotic stromal cells.
Kim KH, Lee EN, Park JK, Lee JR, Kim JH, Choi HJ, Kim BS, Lee HW, Lee KS, Yoon S.
Phytother Res. 2012 Jul;26(7):1037-47.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22183741 - Curcumin ameliorates cardiac inflammation in rats with autoimmune myocarditis.
Mito S, Watanabe K, Harima M, Thandavarayan RA, Veeraveedu PT, Sukumaran V, Suzuki K, Kodama M, Aizawa Y.
Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34(7):974-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21720000 - Curcumin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced renal inflammation.
Zhong F, Chen H, Han L, Jin Y, Wang W.
Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34(2):226-32.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21415532 - Modulation of steroid activity in chronic inflammation: a novel anti-inflammatory role for curcumin.
Biswas S, Rahman I.
Mol Nutr Food Res. 2008 Sep;52(9):987-94.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18327875 - Mechanism of the Anti-inflammatory Effect of Curcumin: PPAR-gamma Activation.
Jacob A, Wu R, Zhou M, Wang P.
PPAR Res. 2007;2007:89369.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18274631 - Anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin, a major constituent of Curcuma longa: a review of preclinical and clinical research.
Jurenka JS.
Altern Med Rev. 2009 Jun;14(2):141-53.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19594223 - Anti-inflammatory effect of curcumin involves downregulation of MMP-9 in blood mononuclear cells.
Saja K, Babu MS, Karunagaran D, Sudhakaran PR.
Int Immunopharmacol. 2007 Dec 15;7(13):1659-67.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17996675 - Curcumin attenuates inflammatory responses of TNF-alpha-stimulated human endothelial cells.
Kim YS, Ahn Y, Hong MH, Joo SY, Kim KH, Sohn IS, Park HW, Hong YJ, Kim JH, Kim W, Jeong MH, Cho JG, Park JC, Kang JC.
J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2007 Jul;50(1):41-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17666914 - Beneficial role of curcumin in skin diseases.
Thangapazham RL, Sharma A, Maheshwari RK.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;595:343-57.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17569219 - Regulation of COX and LOX by curcumin.
Rao CV.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;595:213-26.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17569213 - Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin.
Menon VP, Sudheer AR.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;595:105-25.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17569207 - Effects of curcumin on retinal oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetes.
Kowluru RA, Kanwar M.
Nutr Metab (Lond). 2007 Apr 16;4:8.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17437639 - Curcumin inhibits the expression of COX-2 in UVB-irradiated human keratinocytes (HaCaT) by inhibiting activation of AP-1: p38 MAP kinase and JNK as potential upstream targets.
Cho JW, Park K, Kweon GR, Jang BC, Baek WK, Suh MH, Kim CW, Lee KS, Suh SI.
Exp Mol Med. 2005 Jun 30;37(3):186-92.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16000872 - Inhibition of cyclo-oxygenase 2 expression in colon cells by the chemopreventive agent curcumin involves inhibition of NF-kappaB activation via the NIK/IKK signalling complex.
Plummer SM, Holloway KA, Manson MM, Munks RJ, Kaptein A, Farrow S, Howells L.
Oncogene. 1999 Oct 28;18(44):6013-20.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10557090 - Curcumin blocks cytokine-mediated NF-kappa B activation and proinflammatory gene expression by inhibiting inhibitory factor I-kappa B kinase activity.
Jobin C, Bradham CA, Russo MP, Juma B, Narula AS, Brenner DA, Sartor RB.
J Immunol. 1999 Sep 15;163(6):3474-83.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10477620 - Enhancement of wound healing by curcumin in animals.
Sidhu GS, Singh AK, Thaloor D, Banaudha KK, Patnaik GK, Srimal RC, Maheshwari RK.
Wound Repair Regen. 1998 Mar-Apr;6(2):167-77.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9776860 - In vivo inhibition of nitric oxide synthase gene expression by curcumin, a cancer preventive natural product with anti-inflammatory properties.
Chan MM, Huang HI, Fenton MR, Fong D.
Biochem Pharmacol. 1998 Jun 15;55(12):1955-62.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9714315 - Safety and anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin: a component of tumeric (Curcuma longa).
Chainani-Wu N.
J Altern Complement Med. 2003 Feb;9(1):161-8.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12676044 - Fat digestion and absorption in spice-pretreated rats.
Prakash UN, Srinivasan K.
J Sci Food Agric. 2011 Sep 14.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21918995 - The effect of curcumin and placebo on human gall-bladder function: an ultrasound study.
Rasyid A, Lelo A.
Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1999 Feb;13(2):245-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10102956 - The role of antioxidants and other agents in alleviating hyperglycemia mediated oxidative stress and injury in liver.
Dey A, Lakshmanan J.
Food Funct. 2013 Jun 12.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23760593 - Curcumin prevents alcohol-induced liver disease in rats by inhibiting the expression of NF-kappa B-dependent genes.
Nanji AA, Jokelainen K, Tipoe GL, Rahemtulla A, Thomas P, Dannenberg AJ.
Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003 Feb;284(2):G321-7.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12388178 - Curcumin inhibits NF-kappaB activation and reduces the severity of experimental steatohepatitis in mice.
Leclercq IA, Farrell GC, Sempoux C, dela Peña A, Horsmans Y.
J Hepatol. 2004 Dec;41(6):926-34.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15582125 - Curcumin attenuated paracetamol overdose induced hepatitis.
Somanawat K, Thong-Ngam D, Klaikeaw N.
World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Mar 28;19(12):1962-7.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23569342 - Positive effect of curcumin on inflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction in obese mice with liver steatosis.
Kuo JJ, Chang HH, Tsai TH, Lee TY.
Int J Mol Med. 2012 Sep;30(3):673-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22751848 - Curcumin protects against thioacetamide-induced hepatic fibrosis by attenuating the inflammatory response and inducing apoptosis of damaged hepatocytes.
Wang ME, Chen YC, Chen IS, Hsieh SC, Chen SS, Chiu CH.
J Nutr Biochem. 2012 Oct;23(10):1352-66.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22221674 - Protective effects of curcumin against hepatic fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride: modulation of high-mobility group box 1, Toll-like receptor 4 and 2 expression.
Tu CT, Yao QY, Xu BL, Wang JY, Zhou CH, Zhang SC.
Food Chem Toxicol. 2012 Sep;50(9):3343-51.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22683883 - The protective effect of curcumin on ischemia-reperfusion-induced liver injury.
Lin CM, Lee JF, Chiang LL, Chen CF, Wang D, Su CL.
Transplant Proc. 2012 May;44(4):974-7.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22564600 - Inhibitory effect of curcumin on liver injury in a murine model of endotoxemic shock.
Yun SS, Kim SP, Kang MY, Nam SH.
Biotechnol Lett. 2010 Feb;32(2):209-14.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19856147 - Curcumin adds spice to the debate: lipid metabolism in liver disease.
Graham A.
Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Aug;157(8):1352-3.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19681867 - Curcumin decreased oxidative stress, inhibited NF-kappaB activation, and improved liver pathology in ethanol-induced liver injury in rats.
Samuhasaneeto S, Thong-Ngam D, Kulaputana O, Suyasunanont D, Klaikeaw N.
J Biomed Biotechnol. 2009;2009:981963.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19606259 - Curcumin protects the rat liver from CCl4-caused injury and fibrogenesis by attenuating oxidative stress and suppressing inflammation.
Fu Y, Zheng S, Lin J, Ryerse J, Chen A.
Mol Pharmacol. 2008 Feb;73(2):399-409.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18006644 - Curcumin protects against acute liver damage in the rat by inhibiting NF-kappaB, proinflammatory cytokines production and oxidative stress.
Reyes-Gordillo K, Segovia J, Shibayama M, Vergara P, Moreno MG, Muriel P.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Jun;1770(6):989-96.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17383825 - Therapeutic potential of curcumin in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
Shapiro H, Bruck R.
Nutr Res Rev. 2005 Dec;18(2):212-21.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19079906 - Inhibition by curcumin of diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic hyperplasia, inflammation, cellular gene products and cell-cycle-related proteins in rats.
Chuang SE, Cheng AL, Lin JK, Kuo ML.
Food Chem Toxicol. 2000 Nov;38(11):991-5.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11038236 - Pharmacological actions of curcumin in liver diseases or damage.
Rivera-Espinoza Y, Muriel P.
Liver Int. 2009 Nov;29(10):1457-66.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19811613 - Alcohol metabolites and lipopolysaccharide: roles in the development and/or progression of alcoholic liver disease.
Schaffert CS, Duryee MJ, Hunter CD, Hamilton BC 3rd, DeVeney AL, Huerter MM, Klassen LW, Thiele GM.
World J Gastroenterol. 2009 Mar 14;15(10):1209-18.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19291821 - Nephroprotective and hepatoprotective effects of curcuminoids.
Osawa T.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;595:407-23.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17569222 - Effects of curcumin intake on kidney and liver pathological changes in T2DM rats.
Sun C, Zhang Y, Kong T, Li Y, Feng R, Wang G.
Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2013 Jan;42(1):6-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23596699 - Curcumin prevents liver fat accumulation and serum fetuin-A increase in rats fed a high-fat diet.
Oner-İyidoğan Y, Koçak H, Seyidhanoğlu M, Gürdöl F, Gülçubuk A, Yildirim F, Cevik A, Uysal M.
J Physiol Biochem. 2013 Feb 22.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23430567 - Protective effects of curcumin against oxidative stress parameters and DNA damage in the livers and kidneys of rats with biliary obstruction.
Tokaç M, Taner G, Aydın S, Ozkardeş AB, Dündar HZ, Taşlıpınar MY, Arıkök AT, Kılıç M, Başaran AA, Basaran N.
Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 Jan 29. pii: S0278-6915(13)00053-7.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23376509 - Antioxidative, antiapoptotic, and proliferative effect of curcumin on liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in rats.
Toydemir T, Kanter M, Erboga M, Oguz S, Erenoglu C.
Toxicol Ind Health. 2013 Jan 8.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23299190 - Hepatoprotective effect of curcumin in lipopolysaccharide/-galactosamine model of liver injury in rats: relationship to HO-1/CO antioxidant system.
Fitoterapia. 2011 Jul;82(5):786-91.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21545828 - Efficacy of curcumin to reduce hepatic damage induced by alcohol and thermally treated oil in rats.
El-Deen NA, Eid M.
Vet Ital. 2010 Jan-Mar;46(1):83-92.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20391370 - Curcumin inhibits hepatic protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B and prevents hypertriglyceridemia and hepatic steatosis in fructose-fed rats.
Li JM, Li YC, Kong LD, Hu QH.
Hepatology. 2010 May;51(5):1555-66.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20222050 - Curcumin alleviates ethanol-induced hepatocytes oxidative damage involving heme oxygenase-1 induction.
Bao W, Li K, Rong S, Yao P, Hao L, Ying C, Zhang X, Nussler A, Liu L.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2010 Mar 24;128(2):549-53.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20080166 - Curcumin limits the fibrogenic evolution of experimental steatohepatitis.
Vizzutti F, Provenzano A, Galastri S, Milani S, Delogu W, Novo E, Caligiuri A, Zamara E, Arena U, Laffi G, Parola M, Pinzani M, Marra F.
Lab Invest. 2010 Jan;90(1):104-15.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19901911 - Curcumin prevents liver fibrosis by inducing apoptosis and suppressing activation of hepatic stellate cells.
Shu JC, He YJ, Lv X, Ye GR, Wang LX.
J Nat Med. 2009 Oct;63(4):415-20.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19554395 - Curcumin ameliorates rabbits's steatohepatitis via respiratory chain, oxidative stress, and TNF-alpha.
Ramirez-Tortosa MC, Ramirez-Tortosa CL, Mesa MD, Granados S, Gil A, Quiles JL.
Free Radic Biol Med. 2009 Oct 1;47(7):924-31.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19539747 - Study on antifibrotic effects of curcumin in rat hepatic stellate cells.
Lin YL, Lin CY, Chi CW, Huang YT.
Phytother Res. 2009 Jul;23(7):927-32.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19152370 - Effect of curcumin on the increase in hepatic or brain phosphatidylcholine hydroperoxide levels in mice after consumption of excessive alcohol.
Pyun CW, Han KH, Hong GE, Lee CH.
Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:242671.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23607090 - Detoxification and antioxidant effects of curcumin in rats experimentally exposed to mercury.
Agarwal R, Goel SK, Behari JR.
J Appl Toxicol. 2010 Jul;30(5):457-68.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20229497 - Effect of different curcuminoid supplement dosages on total in vivo antioxidant capacity and cholesterol levels of healthy human subjects.
Pungcharoenkul K, Thongnopnua P.
Phytother Res. 2011 Nov;25(11):1721-6.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21796707 - Randomized double blind study of Curcuma domestica Val. for dyspepsia.
Thamlikitkul V, Bunyapraphatsara N, Dechatiwongse T, Theerapong S, Chantrakul C, Thanaveerasuwan T, Nimitnon S, Boonroj P, Punkrut W, Gingsungneon V, et al.
J Med Assoc Thai. 1989 Nov;72(11):613-20.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2699615 - Effect of oral curcumin administration on serum peroxides and cholesterol levels in human volunteers.
Soni KB, Kuttan R.
Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;36(4):273-5.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1291482 - Effect of curcumin on acidic pH-induced expression of IL-6 and IL-8 in human esophageal epithelial cells (HET-1A): role of PKC, MAPKs, and NF-kappaB.
Rafiee P, Nelson VM, Manley S, Wellner M, Floer M, Binion DG, Shaker R.
Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009 Feb;296(2):G388-98.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19074641 - Chemoprotective effects of curcumin in esophageal epithelial cells exposed to bile acids.
Bower MR, Aiyer HS, Li Y, Martin RC.
World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Sep 7;16(33):4152-8.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20806431 - Comparative antiulcer effect of bisdemethoxycurcumin and curcumin in a gastric ulcer model system.
Mahattanadul S, Nakamura T, Panichayupakaranant P, Phdoongsombut N, Tungsinmunkong K, Bouking P.
Phytomedicine. 2009 Apr;16(4):342-51.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19188055 - Curcumin prevents indomethacin-induced gastropathy in rats.
Thong-Ngam D, Choochuai S, Patumraj S, Chayanupatkul M, Klaikeaw N.
World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Apr 7;18(13):1479-84.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22509079 - Curcuma longa extract protects against gastric ulcers by blocking H2 histamine receptors.
Kim DC, Kim SH, Choi BH, Baek NI, Kim D, Kim MJ, Kim KT.
Biol Pharm Bull. 2005 Dec;28(12):2220-4.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16327153 - Curcumin heals indomethacin-induced gastric ulceration by stimulation of angiogenesis and restitution of collagen fibers via VEGF and MMP-2 mediated signaling.
Sharma AV, Ganguly K, Paul S, Maulik N, Swarnakar S.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012 Feb 15;16(4):351-62.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21942294 - Curcumin suppresses gastric NF-kappaB activation and macromolecular leakage in Helicobacter pylori-infected rats.
Sintara K, Thong-Ngam D, Patumraj S, Klaikeaw N, Chatsuwan T.
World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Aug 28;16(32):4039-46.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20731017 - Investigation of the anti-inflammatory effect of Curcuma longa in Helicobacter pylori-infected patients.
Koosirirat C, Linpisarn S, Changsom D, Chawansuntati K, Wipasa J.
Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Jul;10(7):815-8.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20438867 - Anti-ulcer activity of curcumin on experimental gastric ulcer in rats and its effect on oxidative stress/antioxidant, IL-6 and enzyme activities.
Tuorkey M, Karolin K.
Biomed Environ Sci. 2009 Dec;22(6):488-95.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20337222 - Antimicrobial activity of curcumin against Helicobacter pylori isolates from India and during infections in mice.
De R, Kundu P, Swarnakar S, Ramamurthy T, Chowdhury A, Nair GB, Mukhopadhyay AK.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009 Apr;53(4):1592-7.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19204190 - Preventive action of curcumin in experimental acute pancreatitis in mouse.
Yu WG, Xu G, Ren GJ, Xu X, Yuan HQ, Qi XL, Tian KL.
Indian J Med Res. 2011 Nov;134(5):717-24.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22199113 - Modulation of intestinal mucosal inflammatory factors by curcumin in rats with colitis.
Jian YT, Wang JD, Mai GF, Zhang YL, Lai ZS.
Di Yi Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao. 2004 Dec;24(12):1353-8.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15604057 - Pancreatic stellate cells: new target in the treatment of chronic pancreatitis.
Talukdar R, Tandon RK.
J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008 Jan;23(1):34-41.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17995943 - Anti-inflammatory effects of resveratrol, curcumin and simvastatin in acute small intestinal inflammation.
Bereswill S, Muñoz M, Fischer A, Plickert R, Haag LM, Otto B, Kühl AA, Loddenkemper C, Göbel UB, Heimesaat MM.
PLoS One. 2010 Dec 3;5(12):e15099.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21151942 - IL-1beta causes an increase in intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability.
Al-Sadi RM, Ma TY.
J Immunol. 2007 Apr 1;178(7):4641-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17372023 - Anti-inflammatory effects of dietary phenolic compounds in an in vitro model of inflamed human intestinal epithelium.
Sergent T, Piront N, Meurice J, Toussaint O, Schneider YJ.
Chem Biol Interact. 2010 Dec 5;188(3):659-67.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20816778 - Modulation of neutrophil motility by curcumin: implications for inflammatory bowel disease.
Larmonier CB, Midura-Kiela MT, Ramalingam R, Laubitz D, Janikashvili N, Larmonier N, Ghishan FK, Kiela PR.
Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011 Feb;17(2):503-15.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20629184 - Effects of oral curcumin on indomethacin-induced small intestinal damage in the rat.
Menozzi A, Pozzoli C, Poli E, Martelli M, Martelli L, Zullian C, Bertini S.
Drug Discov Ther. 2009 Apr;3(2):71-6.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22495480 - The effects of dietary curcumin and rutin on colonic inflammation and gene expression in multidrug resistance gene-deficient (mdr1a-/-) mice, a model of inflammatory bowel diseases.
Nones K, Dommels YE, Martell S, Butts C, McNabb WC, Park ZA, Zhu S, Hedderley D, Barnett MP, Roy NC.
Br J Nutr. 2009 Jan;101(2):169-81.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18761777 - Effects of curcumin and Ginkgo biloba on matrix metalloproteinases gene expression and other biomarkers of inflammatory bowel disease.
Motawi TK, Rizk SM, Shehata AH.
J Physiol Biochem. 2012 Dec;68(4):529-39.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22535283 - Tolerability of curcumin in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease: a forced-dose titration study.
Suskind DL, Wahbeh G, Burpee T, Cohen M, Christie D, Weber W.
J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2013 Mar;56(3):277-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23059643 - Curcumin and inflammatory bowel disease: biological mechanisms and clinical implication.
Ali T, Shakir F, Morton J.
Digestion. 2012;85(4):249-55.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22950087 - Effects of curcumin on the intestinal motility of albino rats.
Kumar A, Purwar B, Shrivastava A, Pandey S.
Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010 Jul-Sep;54(3):284-8.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21409867 - Curcumin for inflammatory bowel disease: a review of human studies.
Taylor RA, Leonard MC
Altern Med Rev. 2011 Jun;16(2):152-6.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21649456 - Curcumin inhibits cholesterol uptake in Caco-2 cells by down-regulation of NPC1L1 expression.
Feng D, Ohlsson L, Duan RD.
Lipids Health Dis. 2010 Apr 19;9:40.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20403165 - Curcumin has bright prospects for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease.
Hanai H, Sugimoto K.
Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15(18):2087-94.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19519446 - Clinical utility of curcumin extract.
Asher GN, Spelman K.
Altern Ther Health Med. 2013 Mar-Apr;19(2):20-2.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23594449 - Curcumin attenuates inflammation through inhibition of TLR-4 receptor in experimental colitis.
Lubbad A, Oriowo MA, Khan I.
Mol Cell Biochem. 2009 Feb;322(1-2):127-35.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19002562 - Curcumin reverses attenuated carbachol-induced contraction of the colon in a rat model of colitis.
Lubbad AS, Oriowo MA, Khan I.
Scand J Gastroenterol. 2009;44(2):187-94.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18830899 - Curcumin, an active component of turmeric in the prevention and treatment of ulcerative colitis: preclinical and clinical observations.
Baliga MS, Joseph N, Venkataranganna MV, Saxena A, Ponemone V, Fayad R.
Food Funct. 2012 Nov;3(11):1109-17.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22833299 - Effect of cyclodextrin complexation of curcumin on its solubility and antiangiogenic and anti-inflammatory activity in rat colitis model.
Yadav VR, Suresh S, Devi K, Yadav S.
AAPS PharmSciTech. 2009;10(3):752-62.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19495987 - Effect of dietary turmeric on breath hydrogen.
Shimouchi A, Nose K, Takaoka M, Hayashi H, Kondo T.
Dig Dis Sci. 2009 Aug;54(8):1725-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19034660 - Scientific Evidence and Rationale for the Development of Curcumin and Resveratrol as Nutraceutricals for Joint Health.
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 4202-4232;
Ali Mobasheri, Yves Henrotin, Hans-Konrad Biesalski and Mehdi Shakibaei
PMC: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3344210/pdf/ijms-13-04202.pdf - Curcumin improves bone microarchitecture and enhances mineral density in APP/PS1 transgenic mice.
Yang MW, Wang TH, Yan PP, Chu LW, Yu J, Gao ZD, Li YZ, Guo BL.
Phytomedicine. 2011 Jan 15;18(2-3):205-13.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20637579 - Biological actions of curcumin on articular chondrocytes.
Henrotin Y, Clutterbuck AL, Allaway D, Lodwig EM, Harris P, Mathy-Hartert M, Shakibaei M, Mobasheri A.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010 Feb;18(2):141-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19836480 - Interleukin-1beta-induced extracellular matrix degradation and glycosaminoglycan release is inhibited by curcumin in an explant model of cartilage inflammation.
Clutterbuck AL, Mobasheri A, Shakibaei M, Allaway D, Harris P.
Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009 Aug;1171:428-35.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19723086 - Curcumin inhibits pro-inflammatory mediators and metalloproteinase-3 production by chondrocytes.
Mathy-Hartert M, Jacquemond-Collet I, Priem F, Sanchez C, Lambert C, Henrotin Y.
Inflamm Res. 2009 Dec;58(12):899-908.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19579007 - Natural products as a gold mine for arthritis treatment.
Khanna D, Sethi G, Ahn KS, Pandey MK, Kunnumakkara AB, Sung B, Aggarwal A, Aggarwal BB.
Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2007 Jun;7(3):344-51.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17475558 - Curcumin effects on inflammation and performance recovery following eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage.
Davis JM, Murphy EA, Carmichael MD, Zielinski MR, Groschwitz CM, Brown AS, Gangemi JD, Ghaffar A, Mayer EP.
Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007 Jun;292(6):R2168-73.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17332159 - Anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant properties of Curcuma longa (turmeric) versus Zingiber officinale (ginger) rhizomes in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis.
Ramadan G, Al-Kahtani MA, El-Sayed WM.
Inflammation. 2011 Aug;34(4):291-301.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21120596 - The antioxidants curcumin and quercetin inhibit inflammatory processes associated with arthritis.
Jackson JK, Higo T, Hunter WL, Burt HM.
Inflamm Res. 2006 Apr;55(4):168-75.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16807698 - Turmeric extracts containing curcuminoids prevent experimental rheumatoid arthritis.
Funk JL, Oyarzo JN, Frye JB, Chen G, Lantz RC, Jolad SD, Sólyom AM, Timmermann BN.
J Nat Prod. 2006 Mar;69(3):351-5.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16562833 - Induction of matrix metalloproteinase-13 gene expression by TNF-alpha is mediated by MAP kinases, AP-1, and NF-kappaB transcription factors in articular chondrocytes.
Liacini A, Sylvester J, Li WQ, Huang W, Dehnade F, Ahmad M, Zafarullah M.
Exp Cell Res. 2003 Aug 1;288(1):208-17.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12878172 - Regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokine expression by curcumin in hyaline membrane disease (HMD).
Literat A, Su F, Norwicki M, Durand M, Ramanathan R, Jones CA, Minoo P, Kwong KY.
Life Sci. 2001 Dec 7;70(3):253-67.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12005259 - Efficacy and safety of Meriva®, a curcumin-phosphatidylcholine complex, during extended administration in osteoarthritis patients.
Belcaro G, Cesarone MR, Dugall M, Pellegrini L, Ledda A, Grossi MG, Togni S, Appendino G.
Altern Med Rev. 2010 Dec;15(4):337-44.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21194249 - Curcumin: a new paradigm and therapeutic opportunity for the treatment of osteoarthritis: curcumin for osteoarthritis management.
Henrotin Y, Priem F, Mobasheri A.
Springerplus. 2013 Dec;2(1):56.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23487030 - A randomized, pilot study to assess the efficacy and safety of curcumin in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis.
Chandran B, Goel A.
Phytother Res. 2012 Nov;26(11):1719-25.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22407780 - Short- and long-term exposure of articular cartilage to curcumin or quercetin inhibits aggrecan loss.
Lay E, Samiric T, Handley CJ, Ilic MZ.
J Nutr Biochem. 2012 Feb;23(2):106-12.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21419610 - Curcumin attenuates inflammatory response in IL-1beta-induced human synovial fibroblasts and collagen-induced arthritis in mouse model.
Moon DO, Kim MO, Choi YH, Park YM, Kim GY.
Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 May;10(5):605-10.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20188213 - Differential expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in anterior cruciate ligament and medial collateral ligament fibroblasts after a mechanical injury: involvement of the p65 subunit of NF-kappaB.
Tang Z, Yang L, Xue R, Zhang J, Wang Y, Chen PC, Sung KL.
Wound Repair Regen. 2009 Sep-Oct;17(5):709-16.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19769723 - Oral administration of curcumin suppresses production of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-1 and MMP-3 to ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis: inhibition of the PKCdelta/JNK/c-Jun pathway.
Mun SH, Kim HS, Kim JW, Ko NY, Kim do K, Lee BY, Kim B, Won HS, Shin HS, Han JW, Lee HY, Kim YM, Choi WS.
J Pharmacol Sci. 2009 Sep;111(1):13-21.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19763044 - Decreased activity of neutrophils in the presence of diferuloylmethane (curcumin) involves protein kinase C inhibition.
Jancinová V, Perecko T, Nosál R, Kostálová D, Bauerová K, Drábiková K
Eur J Pharmacol. 2009 Jun 10;612(1-3):161-6.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19371737 - Inhibition effect of curcumin on TNF-α and MMP-13 expression induced by advanced glycation end products in chondrocytes.
Yang Q, Wu S, Mao X, Wang W, Tai H.
Pharmacology. 2013;91(1-2):77-85.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23183190
Le indicazioni sulla salute relative alle piante contenute nei nostri prodotti che compaiono nel nostro sito sono conformi all’elenco delle indicazioni sulla salute in attesa di valutazione definitiva da parte delle autorità della Comunità europea (cfr. Sito della Commissione europea: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/). Possono tuttavia essere soggette a modifica dopo essere state esaminate dalle autorità nazionali competenti.
Le indicazioni sulla salute relative alle altre sostante nutrienti o sostanze contenute nei nostri prodotti che compaiono nel nostro sito sono conformi al regolamento n.° 432/2012 della Commissione europea del 16 maggio 2012 relativo alla compilazione di un elenco di indicazioni sulla salute consentite sui prodotti alimentari, diverse da quelle facenti riferimento alla riduzione dei rischi di malattia e allo sviluppo e alla salute dei bambini (cfr. sito della Commissione europea : http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/).

 Belgique
Belgique  België
België  France
France  Italia
Italia  Portugal
Portugal  España
España  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Κύπρος
Κύπρος