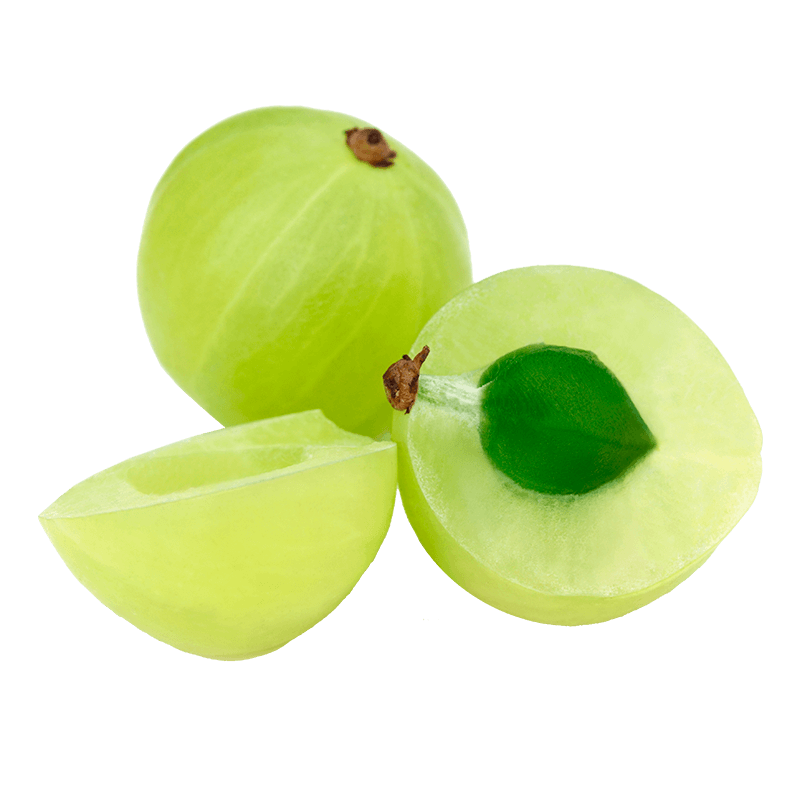
Amla
Latin name
Origin
Used part
Active components
Fibre: suitable for absorbing excess stomach acid.
Tannins: these antioxidant based substances, with astringent properties, protect the gastric mucosa and help in the case of gastric ulcers.
Flavonoids: antioxidants, slow inflammatory reactions.
Vitamin C: antioxidant, neutralises free radicals.
Usage
Bibliographical references
- Amla (Emblica officinalis Gaertn), a wonder berry in the treatment and prevention of cancer.
Baliga MS, Dsouza JJ.
Eur J Cancer Prev. 2011 May;20(3):225-39.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21317655 - Therapeutic Potential of Traditional Chinese Medicine on Inflammatory Diseases.
Tsai WH, Yang CC, Li PC, Chen WC, Chien CT5.
J Tradit Complement Med. 2013 Jul;3(3):142-151.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24716170 - Emblica officinalis (Amla): A review of potential therapeutic applications
Bhandari, Prasan R.; Kamdod, Mohammad Ameeruddin
International Journal of Green Pharmacy;Oct-Dec2012, Vol. 6 Issue 4, p257
International Journal of Green Pharmacy: http://www.greenpharmacy.info/article.asp?issn=0973-8258;year=2012;volume=6;issue=4;spage=257;epage=269;aulast=Bhandari - Amla (Emblica officinalis Gaertn.) extract promotes procollagen production and inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-1 in human skin fibroblasts.
Fujii T, Wakaizumi M, Ikami T, Saito M.
J Ethnopharmacol 2008;119:53-7.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18588964 - Inhibition of UV-induced ROS and collagen damage by Phyllanthus emblica extract in normal human dermal fibroblasts.
Majeed M, Bhat B, Anand S, Sivakumar A, Paliwal P, Geetha KG.
J Cosmet Sci 2011;62:49-56
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21443845 - Effect of Emblica officinalis (fruit) against UVB-induced photo-aging in human skin fibroblasts.
Adil MD, Kaiser P, Satti NK, Zargar AM, Vishwakarma RA, Tasduq SA.
J Ethnopharmacol 2010;132:109-14.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20688142 - Emblica officinalis exerts wound healing action through up-regulation of collagen and extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK1/2).
Sumitra M, Manikandan P, Gayathri VS, Mahendran P, Suguna L.
Wound Repair Regen 2009;17:99-107.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19152656 - Antioxidant activity of tannoid principles of Emblica officinalis (amla) in chronic stress induced changes in rat brain.
Bhattacharya A, Ghosal S, Bhattacharya SK.
Indian J Exp Biol 2000;38:877-80.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12561944 - Possible involvement of monoaminergic neurotransmission in antidepressant-like activity of Emblica officinalis fruits in mice.
Dhingra D, Joshi P, Gupta A, Chhillar R.
CNS Neurosci Ther 2012;18:419-25
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22070517 - Effect of Anwala churna (Emblica officinalis GAERTN.): An ayurvedic preparation on memory deficit rats. Vasudevan M, Parle M.
Yakugaku Zasshi 2007;127:1701-7.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17917427 - Memory enhancing activity of Anwala churna (Emblica officinalis Gaertn.): An Ayurvedic preparation.
Vasudevan M, Parle M.
Physiol Behav 2007;91:46-54
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17343883 - Studies on Emblica officinalis derived tannins for their immunostimulatory and protective activities against coccidiosis in industrial broiler chickens.
Kaleem QM1, Akhtar M2, Awais MM3, Saleem M4, Zafar M5, Iqbal Z1, Muhammad F6, Anwar MI7.
ScientificWorldJournal. 2014 Jan 22;2014:378473.
PMC: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3919087/ - Augmentation of murine natural killer cell and antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity activities by Phyllanthus emblica, a new immunomodulator.
Suresh K, Vasudevan DM.
J Ethnopharmacol 1994;44:55-60
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7990505 - Cyto-protective and immunomodulating properties of Amla (Emblica officinalis) on lymphocytes: An in-vitro study.
Sai Ram M, Neetu D, Yogesh B, Anju B, Dipti P, Pauline T, et al.
J Ethnopharmacol 2002;81:5-10.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12020921 - Biphasic Effect of Phyllanthus emblica L. Extract on NSAID-Induced Ulcer: An Antioxidative Trail Weaved with Immunomodulatory Effect.
Chatterjee A, Chattopadhyay S, Bandyopadhyay SK.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:146808.
PMC: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2976071/ - Healing Properties of Some Indian Medicinal Plants against Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Ulceration of Rats.
Bhattacharya S, Chaudhuri SR, Chattopadhyay S, Bandyopadhyay SK.
J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2007 Sep;41(2):106-14.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18193104 - Gastroprotective effects of 'Amla' Emblica officinalis on in vivo test models in rats.
Al-Rehaily AJ1, Al-Howiriny TA, Al-Sohaibani MO, Rafatullah S.
Phytomedicine. 2002 Sep;9(6):515-22.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12403160 - Antiulcerogenic effect of methanolic extract of Emblica officinalis: an experimental study.
Sairam K1, Rao ChV, Babu MD, Kumar KV, Agrawal VK, K Goel RK.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2002 Sep;82(1):1-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12169398 - The role of antioxidant activity of Phyllanthus emblica fruits on prevention from indomethacin induced gastric ulcer.
Bandyopadhyay SK1, Pakrashi SC, Pakrashi A.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2000 May;70(2):171-6.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10771207 - Antioxidant effect ofPhyllanthus emblica fruits on healing of indomethacin induced gastric ulcer in rats
Anita Pakrashi, Srikanta Pandit, Sandip K. Bandyopadhyay, Satyesh C. Pakrashi
Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry January 2003, Volume 18, Issue 1, pp 15-21
PMC: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3453744/pdf/12291_2008_Article_BF02867660.pdf - Beneficial effects of Emblica officinalis in L-arginine-induced acute pancreatitis in rats.
Sidhu S, Pandhi P, Malhotra S, Vaiphei K, Khanduja KL.
J Med Food 2011;14:147-55
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21138365 - Emblica officinalis: a novel therapy for acute pancreatitis - an experimental study.
Thorat SP1, Rege NN, Naik AS, Thatte UM, Joshi A, Panicker KN, Bapat RD, Dahanukar SA.
HPB Surg. 1995;9(1):25-30.
PMC: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2443754/pdf/HPB-09-025.pdf - Composition and Biological Activities of Hydrolyzable Tannins of Fruits of Phyllanthus emblica.
Yang B, Liu P.
J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Jan 9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24369850 - Antioxidant activity and polyphenol content in edible wild fruits from Nepal.
Chalise JP, Acharya K, Gurung N, et al.
Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2010;61(4):425–432.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20187713 - Antioxidant effect of Phyllanthus emblica extract prevents contrast-induced acute kidney injury.
Tasanarong A1, Kongkham S, Itharat A.
BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Apr 22;14(1):138.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24755233 - Anti-diabetic effects of the Indian indigenous fruit Emblica officinalis Gaertn: active constituents and modes of action.
D'souza JJ1, D'souza PP, Fazal F, Kumar A, Bhat HP, Baliga MS.
Food Funct. 2014 Apr;5(4):635-44.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24577384 - Arsenic-Induced Hepatic Toxicity and Its Attenuation by Fruit Extract of Emblica officinalis (Amla) in Mice.
Singh MK, Dwivedi S, Yadav SS, Sharma P, Khattri S.
Indian J Clin Biochem. 2014 Jan;29(1):29-37.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24478546 - Alcohol-induced oxidative stress in rat liver microsomes: Protective effect of Emblica officinalis.
Reddy VD, Padmavathi P, Hymavathi R, Maturu P, Varadacharyulu NC.
Pathophysiology. 2014 Jan 3. pii: S0928-4680(13)00083-7.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24393670 - Hepatoprotective properties of the Indian gooseberry (Emblica officinalis Gaertn): a review.
Thilakchand KR1, Mathai RT, Simon P, Ravi RT, Baliga-Rao MP, Baliga MS.
Food Funct. 2013 Oct;4(10):1431-41.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23978895 - Roles of Emblica officinalis in Medicine - A Review
K.H. Khan
Botany Research International 2 (4): 218-228, 2009
IDOSI: http://idosi.org/bri/2(4)09/1.pdf - Efficacy of crude extract of Emblica officinalis (amla) in arsenic-induced oxidative damage and apoptosis in splenocytes of mice.
Singh MK, Yadav SS, Yadav RS, Singh US, Shukla Y, Pant KK, Khattri S.
Toxicol Int. 2014 Jan;21(1):8-17.
PMC: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3989920/
The health claims that feature on our website in relation to the plants contained in our products are compliant with the list of health claims awaiting final assessment by the Community authorities (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/). However, they may be subject to modification following their assessment by the national competent authorities.
The health claims relating to other nutrients or substances contained in our products that feature on our site are compliant with Regulation No. 432/2012 of the Commission of 16 May 2012 which establishes a list of authorised health claims authorised in relation to food products, other than those in reference to the reduction of the risk of disease as well as community-based development and child health (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/).

 Belgique
Belgique  België
België  France
France  Italia
Italia  Portugal
Portugal  España
España  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Κύπρος
Κύπρος