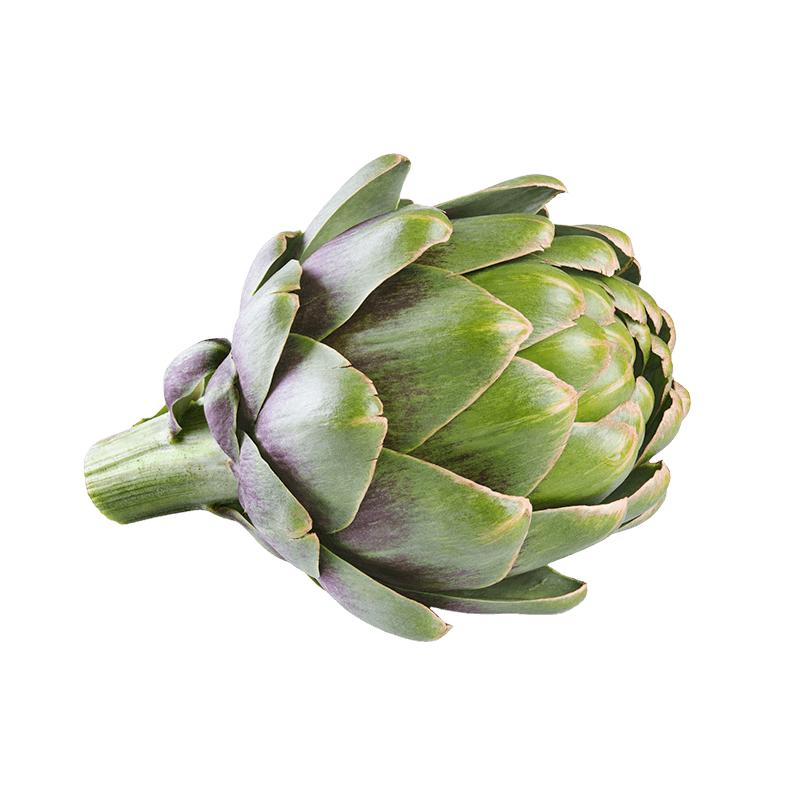
Artichoke
Latin name
Origin
Used part
Active components
Phenolic acids (cynarine, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid): these substances are powerful antioxidants. Cynarine is responsible for the artichoke’s bitter taste and its stimulating effect on the liver, among other properties.
Flavonoids (luteolin): this yellow colourant is also a powerful antioxidant.
Inulin: this sweet tasting polysaccharide is indigestible by humans but contributes to healthy intestinal flora.
Usage
Bibliographical references
- Antioxidative and protective properties of extracts from leaves of the artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) against hydroperoxide-induced oxidative stress in cultured rat hepatocytes.
Gebhardt R.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1997 Jun;144(2):279-86.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9194411
- Increase in choleresis by means of artichoke extract.
Kirchhoff R, Beckers C, Kirchhoff GM, Trinczek-Gärtner H, Petrowicz O, Reimann HJ. Phytomedicine. 1994 Sep;1(2):107-15.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23195882
- Artichoke leaf extract - Recent findings reflecting effects on lipid metabolism, liver and gastrointestinal tracts.
Kraft K.
Phytomedicine. 1997 Dec;4(4):369-78.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23195590
- Anticholestatic activity of flavonoids from artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) and of their metabolites.
Gebhardt R.
Med Sci Monit. 2001 May;7 Suppl 1:316-20.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12211745
- Hepatoprotective activity of polyphenolic compounds from Cynara scolymus against CCl4 toxicity in isolated rat hepatocytes
Adzet T, Camarasa J, Laguna JC.
J Nat Prod. 1987 Jul-Aug;50(4):612-7.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3430163
- Effect of pretreatment with artichoke extract on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury and oxidative stress.
Mehmetçik G, Ozdemirler G, Koçak-Toker N, Cevikbaş U, Uysal M.
Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2008 Sep;60(6):475-80.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18583118
- Choleretic activity and biliary elimination of lipids and bile acids induced by an artichoke leaf extract in rats.
Saénz Rodriguez T, García Giménez D, de la Puerta Vázquez R.
Phytomedicine. 2002 Dec;9(8):687-93.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12587687
- Efficacy of different Cynara scolymus preparations on liver complaints.
Speroni E, Cervellati R, Govoni P, Guizzardi S, Renzulli C, Guerra MC.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2003 Jun;86(2-3):203-11.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12738088
- Protective properties of artichoke (Cynara scolymus) against oxidative stress induced in cultured endothelial cells and monocytes.
Zapolska-Downar D, Zapolski-Downar A, Naruszewicz M, Siennicka A, Krasnodebska B, Kołdziej B.
Life Sci. 2002 Nov 1;71(24):2897-08.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12377270
10. Chem Biol Interact. 2008 May 28;173(2):77-83.
Efficacy of caffeic acid in preventing nickel induced oxidative damage in liver of rats.
Pari L, Prasath A.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18405891
- Liver fibrosis in mice induced by carbon tetrachloride and its reversion by luteolin.
Domitrović R, Jakovac H, Tomac J, Sain I.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009 Dec 15;241(3):311-21.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19747501
- Efficacy of artichoke leaf extract in the treatment of patients with functional dyspepsia: a six-week placebo-controlled, double-blind, multicentre trial.
Holtmann G, Adam B, Haag S, Collet W, Grünewald E, Windeck T.
Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003 Dec;18(11-12):1099-105.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14653829
- Artichoke leaf extract reduces symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome and improves quality of life in otherwise healthy volunteers suffering from concomitant dyspepsia: a subset analysis.
Bundy R, Walker AF, Middleton RW, Marakis G, Booth JC.
J Altern Complement Med. 2004 Aug;10(4):667-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15353023
- A double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over study to establish the bifidogenic effect of a very-long-chain inulin extracted from globe artichoke (Cynara scolymus) in healthy human subjects.
Costabile A, Kolida S, Klinder A, Gietl E, Bäuerlein M, Frohberg C, Landschütze V, Gibson GR.
Br J Nutr. 2010 Oct;104(7):1007-17.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20591206
- Artichoke leaf extract reduces mild dyspepsia in an open study.
Marakis G, Walker AF, Middleton RW, Booth JC, Wright J, Pike DJ.
Phytomedicine. 2002 Dec;9(8):694-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12587688
The health claims that feature on our website in relation to the plants contained in our products are compliant with the list of health claims awaiting final assessment by the Community authorities (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/). However, they may be subject to modification following their assessment by the national competent authorities.
The health claims relating to other nutrients or substances contained in our products that feature on our site are compliant with Regulation No. 432/2012 of the Commission of 16 May 2012 which establishes a list of authorised health claims authorised in relation to food products, other than those in reference to the reduction of the risk of disease as well as community-based development and child health (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/).

 Belgique
Belgique  België
België  France
France  Italia
Italia  Portugal
Portugal  España
España  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Κύπρος
Κύπρος