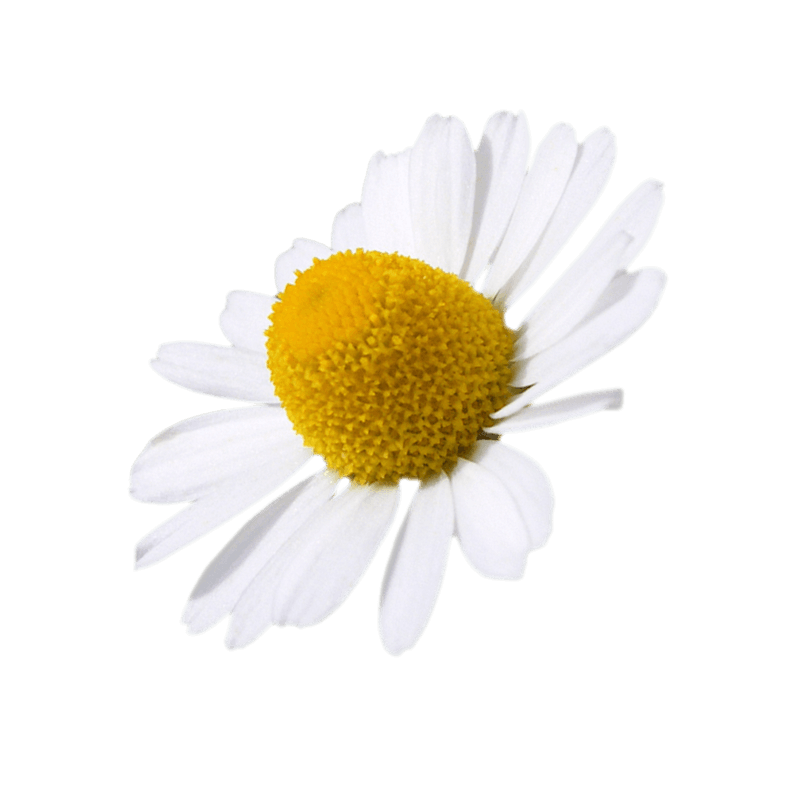
Chamomile (common)
Common chamomile is an annual plant from the asteraceae family.
It is a real pioneer plant, often found near residential areas, heavily used land or grown along roads and fields. It is not a demanding plant, because it can grow perfectly in damp ground and in dry soil. The texture of the soil or its degree of acidity is also not important, contrary to the sunlight, because it does not grow in the shade. The seeds sprout in September and the plant spends the winter with a bouquet of leaves. In the spring, the stems grow vertically to an approximate height of 60 cm, and release several offshoots. The plant can bloom twice a year. The flowers are pedunculate and have white ligulate flowers and light yellow tubular flowers. There are numerous plants that resemble common chamomile. Common chamomile is distinguished by its characteristic flavour of green apples, which is released when you rub the flowers, while the leaves are practically odourless. Moreover, the capitula of common chamomile are hollow. If the leaves of the plant also smell of green apples when rubbed, you are certainly in the presence of Roman chamomile.
Latin name
Origin
Used part
Active components
Sesquiterpenes (α-bisabolol, chamazulene): these components mainly have an anti-inflammatory function, protect the wall of the stomach and also have disinfectant properties.
Flavonoids (apigenin, luteolin): have calming and antispasmodic properties, are antioxidants and have an anti-inflammatory action.
Sesquiterpene lactone (matricin): is responsible for the bitter taste, but also has an anti-inflammatory action.
Coumarin (umbelliferone): has UV absorbing properties and is antibacterial.
Usage
For thousands of years, chamomile was used as a medicinal plant in ancient Egypt, Greece and Rome. It was used as an infusion for a wide variety of digestive disorders. It could also be applied in cases of mouth, throat and eye infections. When dried and powdered, the herb can be spread on the skin to disinfect and accelerate wound healing. The flowers were also used in the past as a room fragrance. The fresh and sweet odour pleasantly fragrances a room, while keeping insects at bay. Today, the essential oil is still used to fragrance cosmetic products and perfumes. In the past, chamomile infusions were used to lighten blonde hair.
A characteristic trait of the essential oil is its dark blue colour. This colour comes from the presence of chamazulene. However, this substance is not naturally contained in the plant, but in the colourless matricin. Thanks to the heat released during the steam distillation extraction process, this substance is transformed into blue chamazulene. Compared with matricin, chamazulene has a less powerful anti-inflammatory action. The supercritical CO2 extraction method produces a dark green oil, for which the transformation into chamazulene has not taken place, and is therefore to be favoured. The liposoluble components of chamomile mainly have an anti-inflammatory and disinfectant action, while the hydrosoluble components have a calming effect, which reduces cramps, and also has a mild disinfectant action. The best chamomile preparations are those that contain both parts. This type of preparation is known as a “totem preparation”. The action of Roman chamomile (chamaemelum nobile) is comparable to that of common chamomile, but is weaker, especially as regards its disinfectant properties. A recent study has demonstrated that chamomile is rich in antioxidants and so protects us against cell damage, while strengthening our resistance. 1-4 It is used in the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders, such as indigestion, mild spasms, bloating, flatulence and reflux. 5-19 Chamomile contributes to optimal mental and physical relaxation, which not only benefits restorative sleep, but also the proper function of the digestive system. 20-24
Bibliographical references
- Determination of the Antioxidant Activity and Stability of Chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla L.) Extract in Sunflower Oil
M.R. Sazegar, A. Banakar, N. Bahrami, A. Bahrami, M. Baghbani, P. Nematolahi and M. Mottaghi
World Applied Sciences Journal 12 (9): 1500-1504, 2011
International Digital Organization for Scientific Information: http://www.idosi.org/wasj/wasj12(9)/20.pdf - Antioxidant activity of water and alcohol extracts of chamomile flowers, anise seeds and dill seeds
Khalid Mohammad Al-Ismail and Talal Aburjai
J Sci Food Agric 84:173–178 (online: 2004)
University of Jordan: http://www2.ju.edu.jo/sites/Academic/aburjai/Lists/Published%20Research/Attachments/27/Abstract.pdf - Elicit of Chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla L.) Extract and Its Antioxidant Activity in Fat-containing Foods
M.R. Sazegar, A. Banakar, N. Bahrami, A. Bahrami, M. Baghbani, S. Asrari
Journal of Applied Chemical Research, 16, 7-14(2011)
Scientific Information Database: http://www.sid.ir/en/VEWSSID/J_pdf/1010820110801.pdf - Comparison of antioxidant activity between two species of chamomiles produced in Xinjiang by TLC-bioautography
Han SL, Li XX, Mian QH, Lan W, Liu Y.
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2013 Jan;38(2):193-8.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23672040 - Gastroprotection of (-)-a-bisabolol on acute gastric mucosal lesions in mice: the possible involved pharmacological mechanisms.
Moura Rocha NF, Venâncio ET, Moura BA, Gomes Silva MI, Aquino Neto MR, Vasconcelos Rios ER, de Sousa DP, Mendes Vasconcelos SM, de França Fonteles MM, de Sousa FC.
Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology 24 (2010) 63–71
Wiley Online Library: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1472-8206.2009.00726.x/abstract?systemMessage=Wiley+Online+Library+will+be+unavailable+for+approximately+4+hours+between+09%3A00+EDT+and+14%3A00+EDT+on+Saturday%2C+28+September+2013+as+we+make+upgrades+to+improve+our+services+to+you.+There+will+also+be+some+delays+to+online+publishing+between+25+to+28+September+2013.+We+apologize+for+the+inconvenience+and+appreciate+your+patience.+Thank+you+for+using+Wiley+Online+Library%21 - (-)-α-Bisabolol attenuates visceral nociception and inflammation in mice.
Leite Gde O, Leite LH, Sampaio Rde S, Araruna MK, de Menezes IR, da Costa JG, Campos AR.
Fitoterapia. 2011 Mar;82(2):208-11.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20875845 - Attenuation of visceral nociception by α-bisabolol in mice: investigation of mechanisms
Gerlânia de Oliveira Leite, Cícera Norma Fernandes, Irwin Rose Alencar de Menezes, José Galberto Martins da Costa and Adriana Rolim Campos
Organic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2012, 2:18
Organic and Medical Chemistry Letters: http://www.orgmedchemlett.com/content/2/1/18 - Biochemical studies on camomile components/III. In vitro studies about the antipeptic activity of (--)-alpha-bisabolol.
Isaac O, Thiemer K.
Arzneimittelforschung. 1975 Sep;25(9):1352-4.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21 - Chamazulene: an antioxidant-type inhibitor of leukotriene B4 formation.
Safayhi H, Sabieraj J, Sailer ER, Ammon HP.
Planta Med. 1994 Oct;60(5):410-3.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7997466 - Effect of dissolution profile and (-)-alpha-bisabolol on the gastrotoxicity of acetylsalicylic acid.
Torrado S, Torrado S, Agis A, Jimenez ME, Cadórniga R.
Pharmazie. 1995 Feb;50(2):141-3.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7700969 - Effect of matricaria recutita on acute pain in the presence and absence of sex hormones
Mahnaz Kesmati, Neda Barfinejad, Hadi Fathi Moghadam
Journal of Research in Medical Sciences July & August 2007; Vol 12, No 4.
MUI Periodicals: http://journals.mui.ac.ir/jrms/article/view/525 - Effects of the herbal formulation ColiMil on upper gastrointestinal transit in mice in vivo.
Capasso R, Savino F, Capasso F.
Phytother Res. 2007 Oct;21(10):999-1101.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17582592 - Evaluation of CNS activities of Matricaria chamomilla l. essential oil in experimental animals from Morocco
Ghizlane Hajjaj, Amina Bounihi, Mouna Tajani, Yahia Cherrah, and Amina Zellou
IJPPS Vol 5, Issue 2, 2013 International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences: http://www.ijppsjournal.com/Vol5Issue2/6691.pdf - Flavonoids inhibit cytokine-induced endothelial cell adhesion protein gene expression.
M. E. Gerritsen, W. W. Carley, G. E. Ranges, C. P. Shen, S. A. Phan, G. F. Ligon, and C. A. Perry
Am J Pathol. 1995 August; 147(2): 278–292.
PMC: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1869822/ - In Vitro Antichemotactic Activity of Chamomilla recutita Hydroethanol Extract
Mayra Marinho Presibella, Cid Aimbiré M.Santos and Almeriane Maria Weffort-Santos
Pharmaceutical Biology, 2007, Vol. 45, No. 2 : Pages 124-130
Informa Healthcare: http://informahealthcare.com/doi/abs/10.1080/13880200601113065 - Pharmacological Studies on Matricaria recutita l. in acute and chronic Inflammation
Parvinder Singh
Department of Pharmacology 2010-2011
Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences: http://www.rguhs.ac.in/cdc/onlinecdc/uploads/04_P027_20713.doc - Pharmacological investigations with compounds of chamomile
V. Jakovlev, O. Isaac, E. Flaskamp
Planta Med 1983; 49(10): 67-73
Thieme E-Journals: https://www.thieme-connect.com/ejournals/abstract/10.1055/s-2007-969818 - A comparative study of the effect of Asacol and the ethanolic extracts of Matricaria chamomilla and Terminalia chebula on induced ulcerative colitis in rabbits
Jinan Abdul-Amir Sabeeh Al-Hussaini, Ahmed Dhahir Latif Al-Hussaini, Aleem Hussein Abd
Kufa Journal For Veterinary Medical Sciences Vol. (3) No. (1) 2012 Iraqi Academic Scientific Journals: http://www.iasj.net/iasj?func=fulltext&aId=62292 - Chamomile: A herbal medicine of the past with bright future
Janmejai K Srivastava, Eswar Shankar and Sanjay Gupta
Mol Med Report. 2010 November 1; 3(6): 895–901.
PMC: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2995283/ - Study of Benzodiazepine Like Effects of Matricaria Recutita on Morphine Withdrawal Syndrome in Adult Male Rats
Kesmati M, Abbasi Zadeh Z, Fathi Moghaddam H
Pak J Med Sci 2008;24(5):735-39.
Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences: http://pjms.com.pk/issues/octdec108/pdf/morphine.pdf - Apigenin, a component of Matricaria recutita flowers, is a central benzodiazepine receptors-ligand with anxiolytic effects.
Viola H, Wasowski C, Levi de Stein M, Wolfman C, Silveira R, Dajas F, Medina JH, Paladini AC.
Planta Med. 1995 Jun;61(3):213-6.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7617761 - Depressive effects of Chamomilla recutita (L.) Rausch, tubular flowers, on central nervous system in mice.
Loggia RD, Traversa U, Scarcia V, Tubaro A.
Pharmacol Res Commun. 1982 Feb;14(2):153-62.
ScienceDirect: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031698982800969 - Pharmacological profile of apigenin, a flavonoid isolated from Matricaria chamomilla.
Avallone R, Zanoli P, Puia G, Kleinschnitz M, Schreier P, Baraldi M.
Biochem Pharmacol. 2000 Jun 1;59(11):1387-94.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10751547 - Flavonoids and the central nervous system: from forgotten factors to potent anxiolytic compounds.
Paladini AC, Marder M, Viola H, Wolfman C, Wasowski C, Medina JH.
J Pharm Pharmacol. 1999 May;51(5):519-26.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10411210
The health claims that feature on our website in relation to the plants contained in our products are compliant with the list of health claims awaiting final assessment by the Community authorities (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/). However, they may be subject to modification following their assessment by the national competent authorities.
The health claims relating to other nutrients or substances contained in our products that feature on our site are compliant with Regulation No. 432/2012 of the Commission of 16 May 2012 which establishes a list of authorised health claims authorised in relation to food products, other than those in reference to the reduction of the risk of disease as well as community-based development and child health (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/).

 Belgique
Belgique  België
België  France
France  Italia
Italia  Portugal
Portugal  España
España  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Κύπρος
Κύπρος