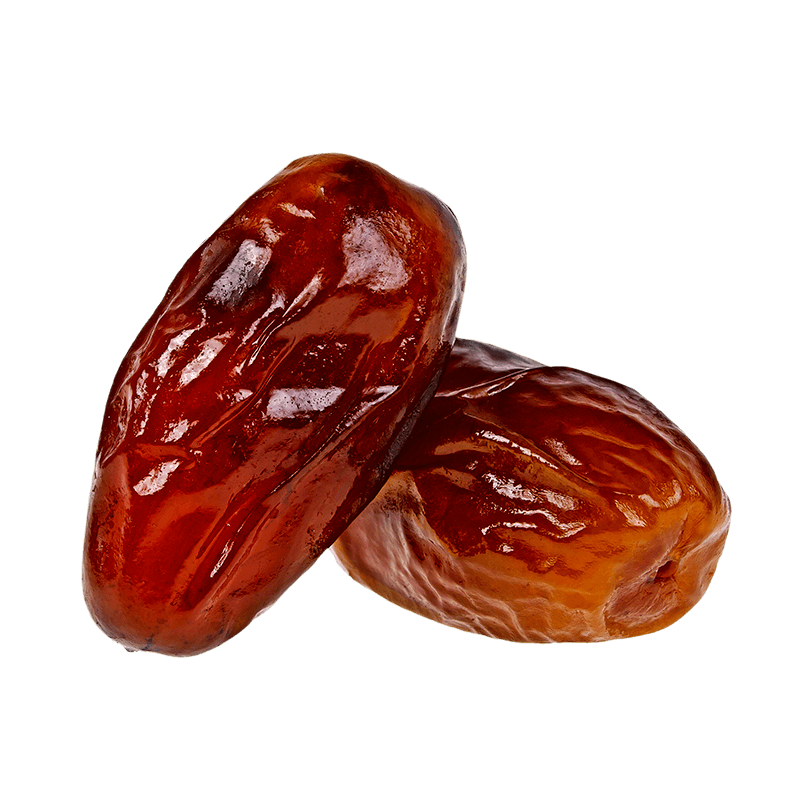
Dates
Latin name
Origin
Used part
Active components
Usage
Bibliographical references
- The fruit of the date palm: its possible use as the best food forthe future?
Al-Shahib W, Marshall RJ.
Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2003 Jul;54(4):247-59.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12850886
- Macrophage Activation and Induction of Macrophage Cytotoxicity byPurified Polysaccharide Fractions from the Plant Echinacea purpurea
Infection and Immunity, Dec. 1984, p. 845-849 Vol. 46, No. 3
M. Stimpel, A. Proksch, H. Wagner, and M.-l. Lohmann Matthes
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6389368
- In vitro effects of echinacea and ginseng on naturalkiller and antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity in healthy subjectsand chronic fatigue syndrome or acquired immunodeficiency syndromepatients.
See DM, Broumand N, Sahl L, Tilles JG.
Immunopharmacology. 1997 Jan;35(3):229-35.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9043936
- Natural killer cells from aging mice treated with extractsfrom Echinacea purpurea are quantitatively and functionallyrejuvenated.
Currier NL, Miller SC.
Exp Gerontol. 2000 Aug;35(5):627-39.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10978684
- Immunopharmacological activity of Echinacea preparationsfollowing simulated digestion on murine macrophages and humanperipheral blood mononuclear cells.
Rininger JA, Kickner S, Chigurupati P, McLean A, Franck Z.
J Leukoc Biol. 2000 Oct;68(4):503-10.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11037971
- Alkylamides of Echinacea purpurea stimulate alveolarmacrophage function in normal rats.
Goel V, Chang C, Slama JV, Barton R, Bauer R, Gahler R, BasuTK.
Int Immunopharmacol. 2002 Feb;2(2-3):381-7.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11811940
- Echinacea stimulates macrophage function in the lung andspleen of normal rats.
Goel V, Chang C, Slama J, Barton R, Bauer R, Gahler R, BasuT.
J Nutr Biochem. 2002 Aug;13(8):487.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12165361
- Enhancement of innate and adaptive immune functions bymultiple Echinacea species.
Zhai Z, Liu Y, Wu L, Senchina DS, Wurtele ES, Murphy PA,Kohut ML, Cunnick JE.
J Med Food. 2007 Sep;10(3):423-34.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17887935
- Enhancement of natural killer cells and increased survivalof aging mice fed daily Echinacea root extract from youth.
Brousseau M, Miller SC.
Biogerontology. 2005;6(3):157-63.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16041619
- Evaluation of echinacea for the prevention and treatmentof the common cold: a meta-analysis.
Shah SA, Sander S, White CM, Rinaldi M, Coleman CI.
Lancet Infect Dis. 2007 Jul;7(7):473-80.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17597571
10. Echinacea in the prevention of induced rhinovirus colds:a meta-analysis.
Schoop R, Klein P, Suter A, Johnston SL.
Clin Ther. 2006 Feb;28(2):174-83.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16678640
- Community Herbal Monograph on Echinacea purpurea (l.)Moench, herba recens
Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products
Doc. Ref. EMEA/HMPC/104945/2006
European Medicines Agency:http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Herbal_-_Community_herbal_monograph/2009/12/WC500018263.pdf
- Planta Med. 1994 Feb;60(1):37-40.
In vitro inhibition of cyclooxygenase and 5-lipoxygenase byalkamides from Echinacea and Achillea species.
Müller-Jakic B, Breu W, Pröbstle A, Redl K, Greger H, BauerR.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8134414
- Echinaforce and other Echinacea fresh plant preparationsin the treatment of the common cold. A randomized, placebocontrolled, double-blind clinical trial.
Brinkeborn RM, Shah DV, Degenring FH.
Phytomedicine. 1999 Mar;6(1):1-6.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10228604
- The efficacy of echinacea compound herbal tea preparationon the severity and duration of upper respiratory and flu symptoms:a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study.
Lindenmuth GF, Lindenmuth EB.
J Altern Complement Med. 2000 Aug;6(4):327-34.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10976979
- Bioactivity of alkamides isolated from Echinacea purpurea(L.) Moench.
Clifford LJ, Nair MG, Rana J, Dewitt DL.
Phytomedicine. 2002 Apr;9(3):249-53.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12046867
- In-vivo and in-vitro anti-inflammatory effect ofEchinacea purpurea and Hypericum perforatum.
Raso GM, Pacilio M, Di Carlo G, Esposito E, Pinto L, Meli R.
J Pharm Pharmacol. 2002 Oct;54(10):1379-83.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12396300
- Antifungal and Anti-inflammatory Activity of the GenusEchinacea
Merali S.; Binns S.; Paulin-Levasseur M.; Ficker C.; SmithM.; Baum B.; Brovelli E.; Arnason J.T.
Pharmaceutical Biology Volume 41, Number 6, September 2003 ,pp. 412-420(9)
Ingenta Connect:http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/tandf/phbi/2003/00000041/00000006/art00003
- A proprietary extract from the Echinacea plant (Echinaceapurpurea) enhances systemic immune response during a common cold.
Goel V, Lovlin R, Chang C, Slama JV, Barton R, Gahler R,Bauer R, Goonewardene L, Basu TK.
Phytother Res. 2005 Aug;19(8):689-94.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16177972
- Macrophage activating effects of new alkamides from theroots of Echinacea species.
Chen Y, Fu T, Tao T, Yang J, Chang Y, Wang M, Kim L, Qu L,Cassady J, Scalzo R, Wang X.
J Nat Prod. 2005 May;68(5):773-6.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15921428
20. Alcohol extracts of Echinacea inhibit production ofnitric oxide and tumor necrosis factor-alpha by macrophages invitro.
Zhai Z, Haney D, Wu L, Solco A, Murphy PA, Wurtele ES, KohutML, Cunnick JE.
Food Agric Immunol. 2007 Sep;18(3-4):221-236.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18458735
- Echinacea species and alkamides inhibit prostaglandinE(2) production in RAW264.7 mouse macrophage cells.
LaLone CA, Hammer KD, Wu L, Bae J, Leyva N, Liu Y, Solco AK,Kraus GA, Murphy PA, Wurtele ES, Kim OK, Seo KI, Widrlechner MP,Birt DF.
J Agric Food Chem. 2007 Sep 5;55(18):7314-22.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17696440
- Echinacea alkylamides modulate induced immune responsesin T-cells.
Matthias A, Banbury L, Bone KM, Leach DN, Lehmann RP.
Fitoterapia. 2008 Jan;79(1):53-8. Epub 2007 Aug 11.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17855021
- Echinacea alkylamides modulate TNF-alpha gene expressionvia cannabinoid receptor CB2 and multiple signal transductionpathways.
Gertsch J, Schoop R, Kuenzle U, Suter A.
FEBS Lett. 2004 Nov 19;577(3):563-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15556647
- Efficacy of Echinacea purpurea in patients with a commoncold. A placebo-controlled, randomised, double-blind clinicaltrial.
Schulten B, Bulitta M, Ballering-Brühl B, Köster U, SchäferM.
Arzneimittelforschung. 2001;51(7):563-8.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11505787
- Macrophage Activation and Induction of Macrophage Cytotoxicity byPurified Polysaccharide Fractions from the Plant Echinacea purpurea
The health claims that feature on our website in relation to the plants contained in our products are compliant with the list of health claims awaiting final assessment by the Community authorities (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/). However, they may be subject to modification following their assessment by the national competent authorities.
The health claims relating to other nutrients or substances contained in our products that feature on our site are compliant with Regulation No. 432/2012 of the Commission of 16 May 2012 which establishes a list of authorised health claims authorised in relation to food products, other than those in reference to the reduction of the risk of disease as well as community-based development and child health (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/).

 Belgique
Belgique  België
België  France
France  Italia
Italia  Portugal
Portugal  España
España  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Κύπρος
Κύπρος