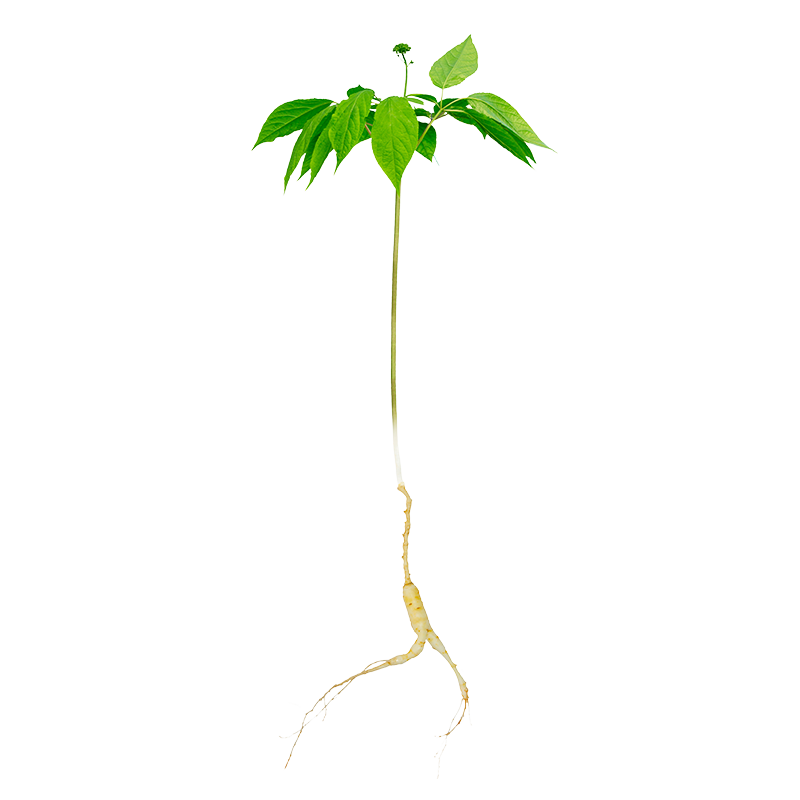
Eleutherococcus
Latin name
Origin
Used part
Active components
Eleutherosides: a complex group of compounds (lignans, sterols, coumarins, saponins) that are responsible for the adaptogenic, stimulating, neuroprotective, hepatoprotective and antioxidant effect.
Polysaccharides: strengthen the immune system.
Polyphenols: antioxidants.
Usage
Bibliographical references
- Intraspecific relationship analysis by DNA markers and in vitrocytotoxic and antioxidant activity in Eleutherococcus senticosus.
Yu CY, Kim SH, Lim JD, Kim MJ, Chung IM.
Toxicol In Vitro. 2003 Apr;17(2):229-36.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12650677
- [Antioxidant properties of a series of extracts frommedicinal plants].
Bol'shakova IV, Lozovskaia EL, Sapezhinskiĭ II.
Biofizika. 1997 Mar-Apr;42(2):480-3.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9172694
- Plant adaptogens increase lifespan and stress resistancein C. elegans.
Wiegant FA, Surinova S, Ytsma E, Langelaar-Makkinje M, WikmanG, Post JA.
Biogerontology. 2009 Feb;10(1):27-42.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18536978
- Antioxidant and immunobiological activity of water-solublepolysaccharide fractions purified from Acanthopanax senticosu.
Chen R, Liu Z, Zhao J, Chen R, Meng F, Zhang M, Ge W.
Food Chem. 2011 Jul 15;127(2):434-40.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23140683
- Anti-oxidant activities of Acanthopanax senticosus stemsand their lignan components.
Lee S, Son D, Ryu J, Lee YS, Jung SH, Kang J, Lee SY, Kim HS,Shin KH.
Arch Pharm Res. 2004 Jan;27(1):106-10.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14969348
- Immunomopharmacological effects of polysaccharides fromAcanthopanax senticosus on experimental animals.
Shen ML, Zhai SK, Chen HL, Luo YD, Tu GR, Ou DW.
Int J Immunopharmacol. 1991;13(5):549-54.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1783468
- Constituents and pharmacological effects of Eucommia andSiberian ginseng.
Deyama T, Nishibe S, Nakazawa Y.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2001 Dec;22(12):1057-70.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11749801
- Flow-cytometric studies with eleutherococcus senticosusextract as an immunomodulatory agent.
Bohn B, Nebe CT, Birr C.
Arzneimittelforschung. 1987 Oct;37(10):1193-6.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2963645
- The influence of active components of Eleutherococcussenticosus on cellular defence
and physical fitness in man
Szołomicki J, Samochowiec L, Wójcicki J, Droździk M
Phytother Res. 2000 Feb;14(1):30-5
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10641044
10. Effects of various Eleutherococcus senticosus cortex onswimming time, natural killer activity and corticosterone level inforced swimming stressed mice
Yoshiyuki Kimura, Maho Sumiyoshi
Journal of Ethnopharmacology Volume 95, Issues 2–3, December2004, Pages 447–453
Sience Direct:http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378874104004234
- The influence of Eleuterococcus senticosus on cellularand humoral immunological response of mice.
Rogala E, Skopińska-Rózewska E, Sawicka T, Sommer E,Prosińska J, Drozd J.
Pol J Vet Sci. 2003;6(3 Suppl):37-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14509359
- [Stimulation of the immunological reactivity of cancerpatients by Eleutherococcus extract].
Kupin VI, Polevaia EB.
Vopr Onkol. 1986;32(7):21-6.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3526720
- Immunopharmacological in vitro effects of Eleutherococcussenticosus extracts.
Steinmann GG, Esperester A, Joller P.
Arzneimittelforschung. 2001 Jan;51(1):76-83.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11215331
- Antiviral activity of an extract derived from roots ofEleutherococcus senticosus.
Glatthaar-Saalmüller B, Sacher F, Esperester A.
Antiviral Res. 2001 Jun;50(3):223-8.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11397509
- Eleutherococcus senticosus extract attenuates LPS-inducediNOS expression through the inhibition of Akt and JNK pathways inmurine macrophage.
Jung CH, Jung H, Shin YC, Park JH, Jun CY, Kim HM, Yim HS,Shin MG, Bae HS, Kim SH, Ko SG.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2007 Aug 15;113(1):183-7.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17644291
- A randomized, controlled study of Kan Jang versusamantadine in the treatment of influenza in Volgograd.
Kulichenko LL, Kireyeva LV, Malyshkina EN, Wikman G.
J Herb Pharmacother. 2003;3(1):77-93.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15277072
- Double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot and phase IIIstudy of activity of standardized Andrographis paniculata HerbaNees extract fixed combination (Kan jang) in the treatment ofuncomplicated upper-respiratory tract infection.
Melchior J, Spasov AA, Ostrovskij OV, Bulanov AE, Wikman G.
Phytomedicine. 2000 Oct;7(5):341-50.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11081985
- A randomized double blind placebo controlled clinicalevaluation of extract of Andrographis paniculata (KalmCold) inpatients with uncomplicated upper respiratory tract infection.
Saxena RC, Singh R, Kumar P, Yadav SC, Negi MP, Saxena VS,Joshua AJ, Vijayabalaji V, Goudar KS, Venkateshwarlu K, Amit A.
Phytomedicine. 2010 Mar;17(3-4):178-85.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20092985
- Controlled clinical study of standardized Andrographispaniculata extract in common cold - a pilot trial
J. Melchior, S. Palm, G. Wikman
Phytomedicine Volume 3, Issue 4, February 1997, Pages 315–318
Science Direct:http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0944711397800025
20. Prevention of common colds with Andrographis paniculatadried extract. A Pilot double blind trial.
Cáceres DD, Hancke JL, Burgos RA, Wikman GK.
Phytomedicine. 1997 Jun;4(2):101-4.
Science Direct: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23195395
- A double-blind study with a new monodrug Kan Jang:Decrease of symptoms and improvement in the recovery from commoncolds
Juan Hancke, Rafael Burgos, Dante Caceres, Georg Wikman
Phytotherapy Research Volume 9, Issue 8, pages 559–562,December 1995
Wiley Online Library:http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ptr.2650090804/abstract
- A double blind, placebo-controlled study of Andrographispaniculata fixed combination Kan Jang in the treatment of acuteupper respiratory tract infections including sinusitis.
Gabrielian ES, Shukarian AK, Goukasova GI, Chandanian GL,Panossian AG, Wikman G, Wagner H.
Phytomedicine. 2002 Oct;9(7):589-97.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12487322
- Comparative controlled study of Andrographis paniculatafixed combination, Kan Jang and an Echinacea preparation asadjuvant, in the treatment of uncomplicated respiratory disease inchildren.
Spasov AA, Ostrovskij OV, Chernikov MV, Wikman G.
Phytother Res. 2004 Jan;18(1):47-53.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14750201
The health claims that feature on our website in relation to the plants contained in our products are compliant with the list of health claims awaiting final assessment by the Community authorities (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/). However, they may be subject to modification following their assessment by the national competent authorities.
The health claims relating to other nutrients or substances contained in our products that feature on our site are compliant with Regulation No. 432/2012 of the Commission of 16 May 2012 which establishes a list of authorised health claims authorised in relation to food products, other than those in reference to the reduction of the risk of disease as well as community-based development and child health (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/).

 Belgique
Belgique  België
België  France
France  Italia
Italia  Portugal
Portugal  España
España  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Κύπρος
Κύπρος