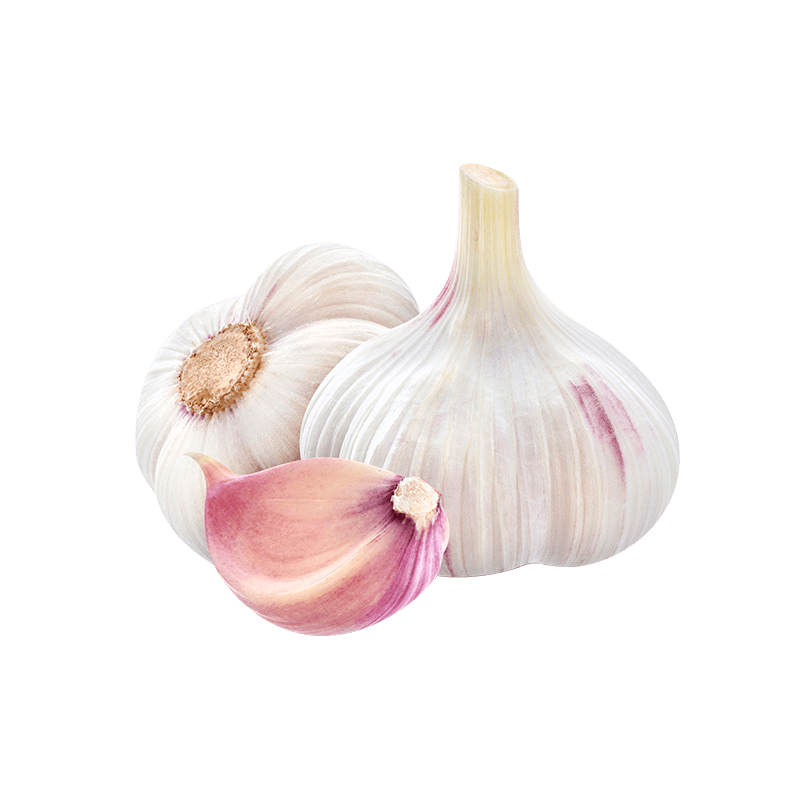
Garlic
Latin name
Origin
Used part
Active components
Saccharides (FOS, inulin): promote the balance of intestinal flora.
Essential oil (allicin, DAS, DADS, DATS, AMS): these volatile-sulphur compounds are the components responsible for most health effects. They have antiseptic, antioxidant, hypotensive, and cholesterol-lowering effects and a protective effect on the cardiovascular system. They are also the components responsible for bad breath in those that take them.
Organic sulphur compounds (SAC, SMC, SAMC): prevent the oxidation of cholesterol and have a hepatoprotective effect.
Usage
All over the world, garlic is one of the most common herbs used to bring out the flavour in a dish. It can significantly contribute to the flavour of numerous dishes. Despite the fact that it is the bulbs that are used, the leaves and the flowers are also edible and have a milder flavour. Garlic has been known since the times of ancient Egypt. Over the centuries, it has been used to treat various conditions such as cardiac and circulatory diseases, arthritis, lung diseases, abdominal tumours, diarrhoea and parasitic infections. Modern science tends to confirm most of the beliefs of ancient cultures. Garlic can help to maintain the microbial balance of the intestinal flora and supports the defence against harmful micro-organisms. 1-5 It has a modulating effect in relation to the immune system. 6-13 Thanks to its antioxidants, it combats both the formation of free radicals, thus slowing the premature ageing of the organism, and the oxidation of cholesterol. 14-19 Garlic contributes to the proper function of the heart, the circulation, the normalisation of cholesterol levels and the reduction of the homocysteine content. 20-25 It also protects the liver against the effects of toxins and ensures the proper function of this organ. 26-40 Garlic also has a positive effect on the metabolism of sugar and increases insulin sensitivity. 41-46 And if you have ever been repulsed by the strong odour, you should know that a recent study discovered that drinking milk at the same time as eating garlic considerably reduces the production of malodorous molecules. 47
Bibliographical references
- Effect of garlic powder on the growth of commensal bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract.
Filocamo A, Nueno-Palop C, Bisignano C, Mandalari G, Narbad A.
Phytomedicine. 2012 Jun 15;19(8-9):707-11.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22480662 - Garlic derivatives (PTS and PTS-O) differently affect the ecology of swine faecal microbiota in vitro.
Ruiz R, García MP, Lara A, Rubio LA.
Vet Microbiol. 2010 Jul 29;144(1-2):110-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20080364 - Antimicrobial effect of garlic (Allium sativum).
Goncagul G, Ayaz E.
Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2010 Jan;5(1):91-3.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19929845 - Antimicrobial activity of garlic, tea tree oil, and chlorhexidine against oral microorganisms.
Groppo FC, Ramacciato JC, Simões RP, Flório FM, Sartoratto A.
Int Dent J. 2002 Dec;52(6):433-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12553397 - The Role of Diallyl Sulfides and Dipropyl Sulfides in the In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of the Essential Oil of Garlic, Allium sativum L., and Leek, Allium porrum L.
Casella S, Leonardi M, Melai B, Fratini F, Pistelli L.
Phytother Res. 2013 Mar;27(3):380-3.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22610968 - Historical Perspective on the Use of Garlic
Richard S. Rivlin
J. Nutr. March 1, 2001 vol. 131 no. 3 951S-954S
The Journal of Nutrition: http://jn.nutrition.org/content/131/3/951S.short - Modulatory effects of two levels of dietary Alliums on immune response and certain immunological variables, following immunization, in White Leghorn chickens.
Hanieh H, Narabara K, Piao M, Gerile C, Abe A, Kondo Y.
Anim Sci J. 2010 Dec;81(6):673-80.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21108687 - Dietary garlic (Allium sativum) lectins, ASA I and ASA II, are highly stable and immunogenic.
Clement F, Venkatesh YP.
Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Oct;10(10):1161-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20615490 - Identity of the immunomodulatory proteins from garlic (Allium sativum) with the major garlic lectins or agglutinins.
Clement F, Pramod SN, Venkatesh YP.
Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Mar;10(3):316-24.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20004743 - The effect of garlic consumption on Th1/Th2 cytokines in phytohemagglutinin (PHA) activated rat spleen lymphocytes.
Zamani A, Vahidinia A, Ghannad MS.
Phytother Res. 2009 Apr;23(4):579-81.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19107745 - Garlic (Allium sativum) extract inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced Toll-like receptor 4 dimerization.
Youn HS, Lim HJ, Lee HJ, Hwang D, Yang M, Jeon R, Ryu JH.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2008 Feb;72(2):368-75.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18256479 - Modulation of cytokine expression by traditional medicines: a review of herbal immunomodulators.
Spelman K, Burns J, Nichols D, Winters N, Ottersberg S, Tenborg M.
Altern Med Rev. 2006 Jun;11(2):128-50.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16813462 - [Study of anti-tumor action and influence on immune function of Allium stativum].
Li Q, Li S, Yang G.
Zhong Yao Cai. 1998 May;21(5):240-3.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12567957 - Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2007 May 30;53(5):63-7.
Allium sativum constituents: effect on free radical generation from rat neutrophils.
Sankaranarayanan A, Narender T, Kumar S, Dikshit M.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17543234 - A comparative study of antioxidants S-allyl cysteine sulfoxide and vitamin E on the damages induced by nicotine in rats.
Helen A, Krishnakumar K, Vijayammal PL, Augusti KT.
Pharmacology. 2003 Mar;67(3):113-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12571405 - Antioxidant role of oils isolated from garlic (Allium sativum Linn) and onion (Allium cepa Linn) on nicotine-induced lipid peroxidation.
Helen A, Rajasree CR, Krishnakumar K, Augusti KT, Vijayammal PL.
Vet Hum Toxicol. 1999 Oct;41(5):316-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10509436 - Garlic compounds protect vascular endothelial cells from oxidized low density lipoprotein-induced injury.
Ide N, Lau BH.
J Pharm Pharmacol. 1997 Sep;49(9):908-11.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9306260 - Raw and boiled garlic enhances plasma antioxidant activity and improves plasma lipid metabolism in cholesterol-fed rats.
Gorinstein S, Leontowicz H, Leontowicz M, Drzewiecki J, Najman K, Katrich E, Barasch D, Yamamoto K, Trakhtenberg S.
Life Sci. 2006 Jan 2;78(6):655-63.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16165163 - Quantitative evaluation of the antioxidant properties of garlic and shallot preparations.
Leelarungrayub N, Rattanapanone V, Chanarat N, Gebicki JM.
Nutrition. 2006 Mar;22(3):266-74.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16500553 - Garlic and cardiovascular disease: a critical review.
Rahman K, Lowe GM.
J Nutr. 2006 Mar;136(3 Suppl):736S-740S.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16484553 - Effect of garlic on cardiovascular disorders: a review
Sanjay K Banerjee, Subir K Maulik
Nutr J. 2002; 1: 4.
PMC: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC139960/ - Cholesterol lowering effects of garlic extracts and organosulphur compounds: Human and animal studies.
Nutrition Journal 2001; 131: 989-993
Yen YY. and Liu L.
Shahrekord University of Medicals Science: http://www.skums.ac.ir/dorsapax/userfiles/file/garlic_liver_phosphatidate_phosphohy_drolase_plasma_lipid_levels_hyperlipidemic_rats.pdf - Involvement of adenosine and standardization of aqueous extract of garlic (Allium sativum Linn.) on cardioprotective and cardiodepressant properties in ischemic preconditioning and myocardial ischemia-reperfusion induced cardiac injury.
Sharma AK, Munajjam A, Vaishnav B, Sharma R, Sharma A, Kishore K, Sharma A, Sharma D, Kumari R, Tiwari A, Singh SK, Gaur S, Jatav VS, Srinivasan BP, Agarwal SS.
J Biomed Res. 2012 Jan;26(1):24-36.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23554727 - Inhibitory effect of novel diallyldisulfide analogs on HMG-CoA reductase expression in hypercholesterolemic rats: CREB as a potential upstream target.
Rai SK, Sharma M, Tiwari M.
Life Sci. 2009 Jul 31;85(5-6):211-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19523964 - Effect of garlic (Allium sativum linn) on serum lipoproteins and lipoprotein cholesterol levels in albino rats rendered hypercholesteremic by feeding cholesterol.
Kamanna VS, Chandrasekhara N.
Lipids. 1982 Jul;17(7):483-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7121209 - Comparative study on the efficacy of Allium sativum (garlic) in reducing some heavy metal accumulation in liver of wistar rats.
Nwokocha CR, Owu DU, Nwokocha MI, Ufearo CS, Iwuala MO.
Food Chem Toxicol. 2012 Feb;50(2):222-6.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22101063 - Garlic and hepatic coccidiosis: prophylaxis or treatment?
Abu-Akkada SS, Oda SS, Ashmawy KI.
Trop Anim Health Prod. 2010 Oct;42(7):1337-43
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20473715 - Protective effect of Allium neapolitanum Cyr. versus Allium sativum L. on acute ethanol-induced oxidative stress in rat liver.
Nencini C, Franchi GG, Cavallo F, Micheli L.
J Med Food. 2010 Apr;13(2):329-35.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20192846 - Amelioration of lead-induced hepatotoxicity by Allium sativum extracts in Swiss albino mice.
Sharma A, Sharma V, Kansal L.
Libyan J Med. 2010 Jan 7;5.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21483544
30. Effect of garlic (Allium sativum) on nickel II or chromium VI induced alterations of glucose homeostasis and hepatic antioxidant status under sub-chronic exposure conditions.
Das Gupta A, Dhara PC, Dhundasi SA, Das KK.
J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2009;20(1):1-14.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19601391 - Ethanol extract of Allium sativum attenuates testicular and liver toxicity induced by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in rats.
Lee SC, Hwang SY, Kim SW, Kim SK.
J Med Food. 2009 Feb;12(1):93-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19298201
32.Aqueous garlic extract attenuates hepatitis and oxidative stress induced by galactosamine/lipoploysaccharide in rats.
El-Beshbishy HA.
Phytother Res. 2008 Oct;22(10):1372-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18570225 - Prevention of CCl4-induced liver damage by ginger, garlic and vitamin E.
Patrick-Iwuanyanwu KC, Wegwu MO, Ayalogu EO.
Pak J Biol Sci. 2007 Feb 15;10(4):617-21.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19069545 - Hepatoprotective effect of allicin on tissue defense system in galactosamine/endotoxin challenged rats.
Vimal V, Devaki T.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2004 Jan;90(1):151-4.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14698523 - Therapeutic effect of S-allylmercaptocysteine on acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice.
Sumioka I, Matsura T, Yamada K.
Eur J Pharmacol. 2001 Dec 21;433(2-3):177-85.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11755151
36. Inhibition of chemically induced liver carcinogenesis in Wistar rats by garlic (Allium sativum).
Samaranayake MD, Wickramasinghe SM, Angunawela P, Jayasekera S, Iwai S, Fukushima S.
Phytother Res. 2000 Nov;14(7):564-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11054854 - S-methylcysteine and cysteine are inhibitors of induction of glutathione S-transferase placental form-positive foci during initiation and promotion phases of rat hepatocarcinogenesis.
Takada N, Yano Y, Wanibuchi H, Otani S, Fukushima S.
Jpn J Cancer Res. 1997 May;88(5):435-42.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9247599 - Chemoprotection of garlic extract toward cyclophosphamide toxicity in mice.
Unnikrishnan MC, Soudamini KK, Kuttan R.
Nutr Cancer. 1990;13(3):201-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2308875 - Effect of diallyl sulfide on rat liver microsomal nitrosamine metabolism and other monooxygenase activities.
Brady JF, Li DC, Ishizaki H, Yang CS.
Cancer Res. 1988 Nov 1;48(21):5937-40.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3167846 - A study on the effect of garlic to the heavy metal poisoning of rat.
Cha CW.
J Korean Med Sci. 1987 Dec;2(4):213-24.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3268178
41. Effects of garlic oil and diallyl trisulfide on glycemic control in diabetic rats.
Liu CT, Hse H, Lii CK, Chen PS, Sheen LY.
Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 Jun 1;516(2):165-73.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15936752 - Antidiabetic effects of ajoene in genetically diabetic KK-A(y) mice.
Journal of nutritional science and vitaminology. 2005 Oct;51(5):382-4
Hattori A, Yamada N, Nishikawa T, Fukuda H, Fujino T.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16392712
43. Compared ability of garlic (Allium sativum) extract or α-tocopherol + magnesium association to reduce metabolic disorders and oxidative stress in diabetic rats.
Hfaiedh N, Murat JC, Elfeki A.
Phytother Res. 2011 Jun;25(6):821-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21086547 - Effect of methanolic extract of Allium sativum (AS) in delaying cataract in STZ-induced diabetic rats.
Raju TN, Kanth VR, Lavanya K.
J Ocul Biol Dis Infor. 2008 Mar;1(1):46-54.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20072634 - Antidiabetic effect of garlic (Allium sativum L.) in normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.
Eidi A, Eidi M, Esmaeili E.
Phytomedicine. 2006 Nov;13(9-10):624-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17085291 - Antihyperglycemic, antihyperlipidemic, anti-inflammatory and adenosine deaminase- lowering effects of garlic in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with obesity.
Kumar R, Chhatwal S, Arora S, Sharma S, Singh J, Singh N, Bhandari V, Khurana A.
Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2013;6:49-56.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23378779 - Effect of milk on the deodorization of malodorous breath after garlic ingestion.
Hansanugrum A, Barringer SA.
J Food Sci. 2010 Aug 1;75(6):C549-58.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20722910
The health claims that feature on our website in relation to the plants contained in our products are compliant with the list of health claims awaiting final assessment by the Community authorities (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/). However, they may be subject to modification following their assessment by the national competent authorities.
The health claims relating to other nutrients or substances contained in our products that feature on our site are compliant with Regulation No. 432/2012 of the Commission of 16 May 2012 which establishes a list of authorised health claims authorised in relation to food products, other than those in reference to the reduction of the risk of disease as well as community-based development and child health (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/).

 Belgique
Belgique  België
België  France
France  Italia
Italia  Portugal
Portugal  España
España  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Κύπρος
Κύπρος