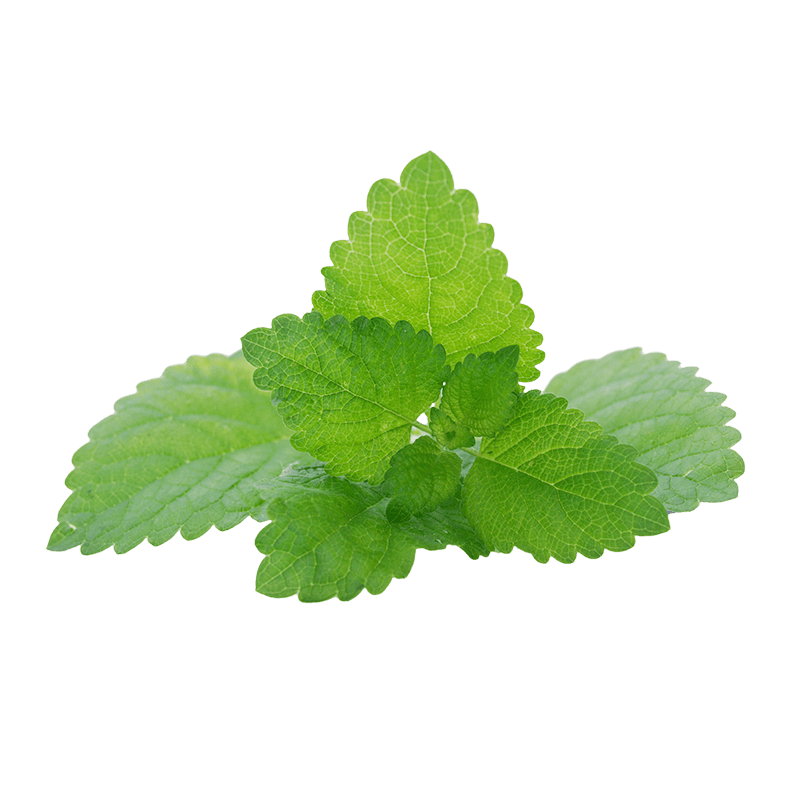
Lemon balm
Latin name
Origin
Used part
Active components
Phenolic acids (rosmarinic acids): these substances with antioxidant properties are responsible for the anxiolytic and calming effect.
Essential oil: responsible for the aroma and contributes to the antioxidant action.
Flavonoids (apigenin): antioxidant.
Usage
The fresh or dried leaves can be used to prepare a herbal tea, and can be blended with black tea. Lemon balm is used as seasoning in numerous recipes such as fish, soup, sauces and omelettes. It has a natural preservative action. The essential oil is sometimes used to repel mosquitoes and other insects. Thanks to its antioxidant action, lemon balm protects the tissues against oxidative stress. 1-6What makes the plant interesting is its calming effect in the case of stress. It supports good cognitive function, well-being and contributes to restorative sleep. 7-14It is also used to support digestion and relieve intestinal cramps. 15-16
Bibliographical references
- Neuroprotective properties of Melissa officinalis afterhypoxic-ischemic injury both in vitro and in vivo.
Bayat M, Azami Tameh A, Hossein Ghahremani M, Akbari M, MehrSE, Khanavi M, Hassanzadeh G.
Daru. 2012 Oct 3;20(1):42.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23351182
- Protective effect of Melissa officinalis aqueous extractagainst Mn-induced oxidative stress in chronically exposed mice.
Martins EN, Pessano NT, Leal L, Roos DH, Folmer V, Puntel GO,Rocha JB, Aschner M, Ávila DS, Puntel RL.
Brain Res Bull. 2012 Jan 4;87(1):74-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22020131
- Antioxidant capacity and total phenolic contents oforegano (Origanum vulgare), lavender (Lavandula angustifolia) andlemon balm (Melissa officinalis) from Romania.
Spiridon I, Colceru S, Anghel N, Teaca CA, Bodirlau R, ArmatuA.
Nat Prod Res. 2011 Oct;25(17):1657-61.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21707233
- Neuroprotective and neurological properties of Melissaofficinalis.
López V, Martín S, Gómez-Serranillos MP, Carretero ME, JägerAK, Calvo MI.
Neurochem Res. 2009 Nov;34(11):1955-61.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19760174
- Radical scavenging, antibacterial, and antiproliferativeactivities of Melissa officinalis L. extracts.
Canadanović-Brunet J, Cetković G, Djilas S, Tumbas V,Bogdanović G, Mandić A, Markov S, Cvetković D, Canadanović V.
J Med Food. 2008 Mar;11(1):133-43.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18361749
- Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Melissaofficinalis L. (Lamiaceae) essential oil.
Mimica-Dukic N, Bozin B, Sokovic M, Simin N.
J Agric Food Chem. 2004 May 5;52(9):2485-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15113145
- Attenuation of laboratory-induced stress in humans afteracute administration of Melissa officinalis (Lemon Balm).
Kennedy DO, Little W, Scholey AB.
Psychosom Med. 2004 Jul-Aug;66(4):607-13.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15272110
- Bioassay-guided fractionation of lemon balm (Melissaofficinalis L.) using an in vitro measure of GABA transaminaseactivity.
Awad R, Muhammad A, Durst T, Trudeau VL, Arnason JT.
Phytother Res. 2009 Aug;23(8):1075-81.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19165747
- Pilot trial of Melissa officinalis L. leaf extract in thetreatment of volunteers suffering from mild-to-moderate anxietydisorders and sleep disturbances.
Cases J, Ibarra A, Feuillère N, Roller M, Sukkar SG.
Med J Nutrition Metab. 2011 Dec;4(3):211-218.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22207903
10. Effects of chronic administration of Melissa officinalisL. extract on anxiety-like reactivity and on circadian andexploratory activities in mice.
Ibarra A, Feuillere N, Roller M, Lesburgere E, Beracochea D.
Phytomedicine. 2010 May;17(6):397-403.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20171069
- Effects of traditionally used anxiolytic botanicals onenzymes of the γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) system.
Authors: Awad, R.; Levac, D.; Cybulska, P.; Merali, Z.;Trudeau, V.L.; Arnason, J.T.
Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology, Volume 85,Number 9, September 2007 , pp. 933-942(10)
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18066140
- Modulation of mood and cognitive performance followingacute administration of single doses of Melissa officinalis (Lemonbalm) with human CNS nicotinic and muscarinic receptor-bindingproperties.
Kennedy DO, Wake G, Savelev S, Tildesley NT, Perry EK, WesnesKA, Scholey AB.
Neuropsychopharmacology. 2003 Oct;28(10):1871-81.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12888775
- Neurotropic action of the hydroalcoholic extract ofMelissa officinalis in the mouse.
Soulimani R, Fleurentin J, Mortier F, Misslin R, Derrieu G,Pelt JM.
Planta Med. 1991 Apr;57(2):105-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1891490
- Anxiolytic and antidepressant-like effects of Melissaofficinalis (lemon balm) extract in rats: Influence ofadministration and gender.
Taiwo AE, Leite FB, Lucena GM, Barros M, Silveira D, SilvaMV, Ferreira VM.
Indian J Pharmacol. 2012 Mar;44(2):189-92.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22529473
- Protective role of Melissa officinalis L. extract onliver of hyperlipidemic rats: a morphological and biochemicalstudy.
Bolkent S, Yanardag R, Karabulut-Bulan O, Yesilyaprak B.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2005 Jul 14;99(3):391-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15946812
- Relaxant effect of essential oil of Melissa officinalisand citral on rat ileum contractions.
Sadraei H, Ghannadi A, Malekshahi K.
Fitoterapia. 2003 Jul;74(5):445-52.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12837359
The health claims that feature on our website in relation to the plants contained in our products are compliant with the list of health claims awaiting final assessment by the Community authorities (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/). However, they may be subject to modification following their assessment by the national competent authorities.
The health claims relating to other nutrients or substances contained in our products that feature on our site are compliant with Regulation No. 432/2012 of the Commission of 16 May 2012 which establishes a list of authorised health claims authorised in relation to food products, other than those in reference to the reduction of the risk of disease as well as community-based development and child health (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/).

 Belgique
Belgique  België
België  France
France  Italia
Italia  Portugal
Portugal  España
España  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Κύπρος
Κύπρος