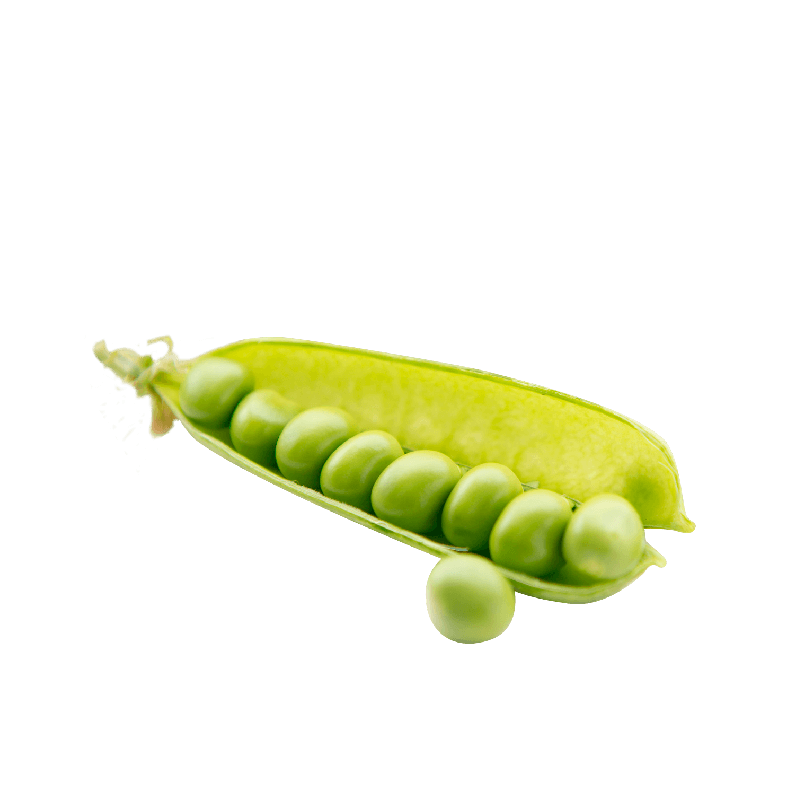
Pea
Latin name
Origin
Used part
Active components
Usage
Bibliographical references
- Bifidogenic effect of dietary fiber and resistant starch fromleguminous on the intestinal microbiota of rats.
da S Queiroz-Monici K, Costa GE, da Silva N, Reis SM, deOliveira AC.
Nutrition. 2005 May;21(5):602-8.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15850967
- Digestion of fibre polysaccharides of pea (Pisum sativum)hulls, carrot and cabbage by adult cockerels.
Longstaff M, McNab JM.
Br J Nutr. 1989 Nov;62(3):563-77.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2557886 - Bifidogenic effect of dietary fiber and resistant starchfrom leguminous on the intestinal microbiota of rats.
da S Queiroz-Monici K, Costa GE, da Silva N, Reis SM, deOliveira AC.
Nutrition. 2005 May;21(5):602-8.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15850967
- Digestion of fibre polysaccharides of pea (Pisum sativum)hulls, carrot and cabbage by adult cockerels.
Longstaff M, McNab JM.
Br J Nutr. 1989 Nov;62(3):563-77.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2557886
The health claims that feature on our website in relation to the plants contained in our products are compliant with the list of health claims awaiting final assessment by the Community authorities (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/). However, they may be subject to modification following their assessment by the national competent authorities.
The health claims relating to other nutrients or substances contained in our products that feature on our site are compliant with Regulation No. 432/2012 of the Commission of 16 May 2012 which establishes a list of authorised health claims authorised in relation to food products, other than those in reference to the reduction of the risk of disease as well as community-based development and child health (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/).

 Belgique
Belgique  België
België  France
France  Italia
Italia  Portugal
Portugal  España
España  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Κύπρος
Κύπρος