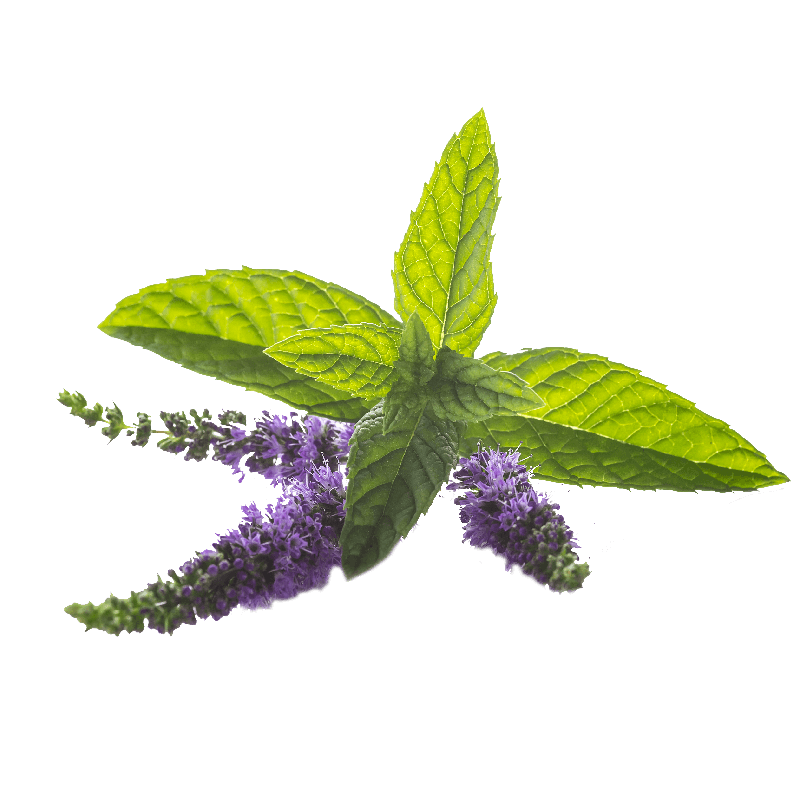
Peppermint
Latin name
Origin
Used part
Active components
Essential oil (menthol, menthone): It has a vast scope of action. To combat cramps, fight bacteria, stimulate the production of bile, dissipate intestinal gases, provide calm, ease pain and promote digestion.
Tannins: Antibacterial action.
Flavonoids: Antioxidant action.
Phenolic acids: Antioxidant action.
Usage
Bibliographical references
- Herbal remedies for dyspepsia: peppermint seems effective.
[No authors listed]
Prescrire Int. 2008 Jun;17(95):121-3.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18630390 - Antiemetic activity of volatile oil from Mentha spicata and Mentha × piperita in chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting
Z Tayarani-Najaran, E Talasaz-Firoozi, R Nasiri, N Jalali and MK Hassanzadeh
Ecancermedicalscience. 2013; 7: 290.
PMC: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3562057/ - Mode of Action of Peppermint Oil and (-)-Menthol with Respect to 5-HT3 Receptor
Subtypes: Binding Studies, Cation Uptake by Receptor Channels and Contraction of Isolated
Rat Ileum
Katharina Heimes, Florian Hauk and Eugen J. Verspohl
Phytother. Res. 25: 702–708 (2011)
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21077259 - Aromatherapy for treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting (Review)
Hines S, Steels E, Chang A, Gibbons K
ePrints: http://eprints.qut.edu.au/54475/4/54475b.pdf - Peppermint oil: a treatment for postoperative nausea
Tate S.
J Adv Nurs. 1997 Sep;26(3):543-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9378876 - Preliminary experimental research on the mechanism of liver bile secretion stimulated by peppermint oil.
Zong L, Qu Y, Luo DX, Zhu ZY, Zhang S, Su Z, Shan JC, Gao XP, Lu LG.
J Dig Dis. 2011 Aug;12(4):295-301.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21791024 - Folium Menthae Piperitae
WHO Monographs on Selected Medicinal Plants - Volume 2 (2004)
WHO: http://apps.who.int/medicinedocs/es/d/Js4927e/20.html#Js4927e.20 - Efficacy of Peppermint oil in diarrhea predominant IBS - a double blind randomized placebo - controlled study.
Alam MS, Roy PK, Miah AR, Mollick SH, Khan MR, Mahmud MC, Khatun S.
Mymensingh Med J. 2013 Jan;22(1):27-30.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23416804 - Gastrointestinal clinical pharmacology of peppermint oil
H.-G. Grigoleit, P. Grigoleit
Phytomedicine 12 (2005) 607–611
ScienceDirect: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0944711305001066 - Peppermint oil (Mintoil®) in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: A prospective double blind placebo-controlled randomized trial
G. Cappello, M. Spezzaferro, L. Grossi, L. Manzoli, L. Marzio
Digestive and Liver Disease 39 (2007) 530–536
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17420159 - Peppermint oil in irritable bowel syndrome
H.-G. Grigoleit,P. Grigoleit
Phytomedicine 12 (2005) 601–606
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16121521 - The Treatment of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth With Enteric-Coated Peppermint
Oil: A Case Report
Alan C. Logan and Tracey M. Beaulne
Alternative Medicine Review Volume 7, Number 5 (2002)
Alternative Medicine Review: http://www.altmedrev.com/publications/7/5/410.pdf - Antibacterial effects of the essential oils of commonly consumed medicinal herbs using an in vitro model.
Soković M, Glamočlija J, Marin PD, Brkić D, van Griensven LJ.
Molecules. 2010 Oct 27;15(11):7532-46.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21030907 - Protective effects of bioactive phytochemicals from Mentha piperita with multiple health potentials.
Sharafi SM, Rasooli I, Owlia P, Taghizadeh M, Astaneh SD.
Pharmacogn Mag. 2010 Jul;6(23):147-53.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20931070 - Evaluation of antibacterial activity of selected Iranian essential oils against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli in nutrient broth medium.
Mohsenzadeh M.
Pak J Biol Sci. 2007 Oct 15;10(20):3693-7.
Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences: http://198.170.104.138/pjbs/2007/3693-3697.pdf - Anti-Candida activity of Brazilian medicinal plants.
Duarte MC, Figueira GM, Sartoratto A, Rehder VL, Delarmelina C.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2005 Feb 28;97(2):305-11.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15707770 - Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of three Mentha species essential oils.
Mimica-Dukić N, Bozin B, Soković M, Mihajlović B, Matavulj M.
Planta Med. 2003 May;69(5):413-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12802721 - Inhibition by the essential oils of peppermint and spearmint of the growth of pathogenic bacteria.
Imai H, Osawa K, Yasuda H, Hamashima H, Arai T, Sasatsu M.
Microbios. 2001;106 Suppl 1:31-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11549238 - Enteric-coated peppermint-oil capsules in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a prospective, randomized trial.
Liu JH, Chen GH, Yeh HZ, Huang CK, Poon SK.
J Gastroenterol. 1997 Dec;32(6):765-8.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9430014 - Potential pharmacological and toxicological basis of the essential oil from Mentha spp
Peixoto, I.T.A.; Furlanetti, V.F.; Anibal, P.C.; Duarte, M.C.T.; Höfling, J.F.
Rev Ciênc Farm Básica Apl., 2009;30(3):235-239
Universidade Estadual Paulista Júlio de Mesquita Filho:
http://serv-bib.fcfar.unesp.br/seer/index.php/Cien_Farm/article/viewFile/800/889
The health claims that feature on our website in relation to the plants contained in our products are compliant with the list of health claims awaiting final assessment by the Community authorities (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/). However, they may be subject to modification following their assessment by the national competent authorities.
The health claims relating to other nutrients or substances contained in our products that feature on our site are compliant with Regulation No. 432/2012 of the Commission of 16 May 2012 which establishes a list of authorised health claims authorised in relation to food products, other than those in reference to the reduction of the risk of disease as well as community-based development and child health (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/).

 Belgique
Belgique  België
België  France
France  Italia
Italia  Portugal
Portugal  España
España  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Κύπρος
Κύπρος