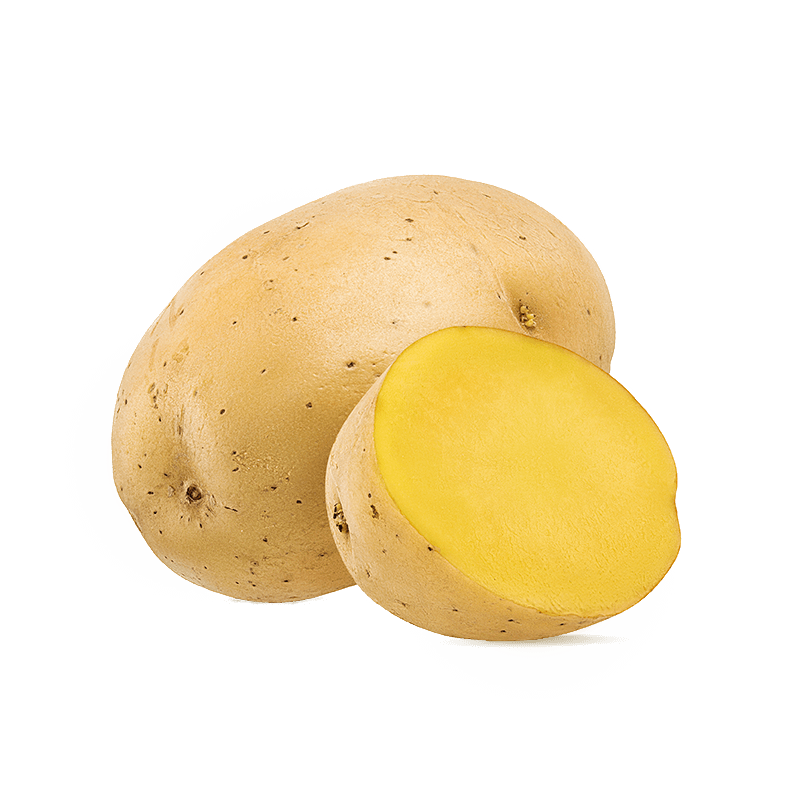
Potato
Latin name
Origin
Used part
Active components
Usage
Like the other members of the solanaceae family, all of the green parts of the potato plant are toxic. However, the tubers are edible as long as they are not exposed to too much light, because they may then contain toxic quantities of solanine. Potatoes are an important source of carbohydrates. It is therefore one of the most commonly cultivated foods in the world. Its vitamin, mineral and fibre content makes it a healthy vegetable. Potato starch is a fundamental ingredient in the production of vodka, but also for biodegradable plastic. Freshly pressed potato juice is used as a traditional remedy for hyperacidity problems in Germany and Switzerland, due to its supposed antispasmodic and antacid effects. 1,2
Bibliographical references
- Efficacy and tolerability of potato juice in dyspeptic patients: a pilot study. Chrubasik S, Chrubasik C, Torda T, Madisch A. Phytomedicine. 2006 Jan;13(1-2):11-5. Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16360927
- Further evidence on the effectiveness of potato juice in dyspeptic complaints. Chrubasik S, Boyko T, Filippov Y, Torda T. The Free Library: http://www.thefreelibrary.com/Further+evidence+on+the+effectiveness+of+potato+juice+in+dyspeptic...-a0153402776
The health claims that feature on our website in relation to the plants contained in our products are compliant with the list of health claims awaiting final assessment by the Community authorities (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/). However, they may be subject to modification following their assessment by the national competent authorities.
The health claims relating to other nutrients or substances contained in our products that feature on our site are compliant with Regulation No. 432/2012 of the Commission of 16 May 2012 which establishes a list of authorised health claims authorised in relation to food products, other than those in reference to the reduction of the risk of disease as well as community-based development and child health (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/).

 Belgique
Belgique  België
België  France
France  Italia
Italia  Portugal
Portugal  España
España  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Κύπρος
Κύπρος