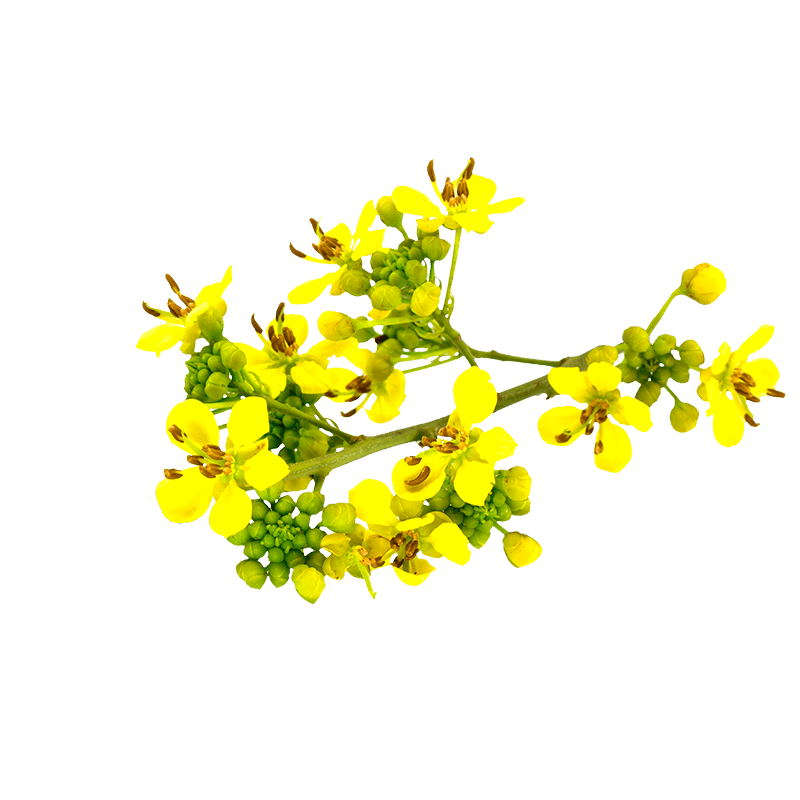
Senna
Latin name
Origin
Used part
Active components
Usage
Bibliographical references
- Cathartic activity of Cassia species.
Ahmed S, Qureshi S, Kapadia Z, Badar Y, 1989.
Pak J Pharm Sci, 2, 37-45.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16414646
- Monographie der Kommission E, 1993. Bundesanzeiger, 133.
- Community Herbal Monograph on Senna Leaf (Sennae Folium). EMEA (European Medicines Agency), 2006. Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products
Doc. Ref. EMEA/HMPC/51869/2006
EMEA: http://www.emea.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Herbal_-_Community_herbal_monograph/2009/12/WC500018210.pdf
- Safety and efficacy of a bulk laxative containing senna versus lactulose in the treatment of chronic constipation in geriatric patients.
Kinnunen O, Winblad I, Koistinen P, Salokannel J.
Pharmacology. 1993 Oct;47 Suppl 1:253-5.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8234438
- Myths and misconceptions about chronic constipation.
Müller-Lissner SA, Kamm MA, Scarpignato C, Wald A.
Am J Gastroenterol. 2005 Jan;100(1):232-42.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15654804
- Cassia angustifolia extract is not hepatotoxic in an in vitro and in vivo study.
Vitalone A, Di Giacomo S, Di Sotto A, Franchitto A, Mammola CL, Mariani P, Mastrangelo S, Mazzanti G.
Pharmacology. 2011;88(5-6):252-9.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21997710
- Is senna laxative use associated to cathartic colon, genotoxicity, or carcinogenicity?
Morales MA, Hernández D, Bustamante S, Bachiller I, Rojas A.
J Toxicol. 2009;2009:287247.
Hindawi: http://www.hindawi.com/journals/jt/2009/287247/
- Anthraquinones Containing Plants Reconsidered
L. Delmulle, K. Demeyer
ISBN: 9789034192905, WPG Uitgevers BE, 2008
The health claims that feature on our website in relation to the plants contained in our products are compliant with the list of health claims awaiting final assessment by the Community authorities (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/). However, they may be subject to modification following their assessment by the national competent authorities.
The health claims relating to other nutrients or substances contained in our products that feature on our site are compliant with Regulation No. 432/2012 of the Commission of 16 May 2012 which establishes a list of authorised health claims authorised in relation to food products, other than those in reference to the reduction of the risk of disease as well as community-based development and child health (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/).

 Belgique
Belgique  België
België  France
France  Italia
Italia  Portugal
Portugal  España
España  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Κύπρος
Κύπρος